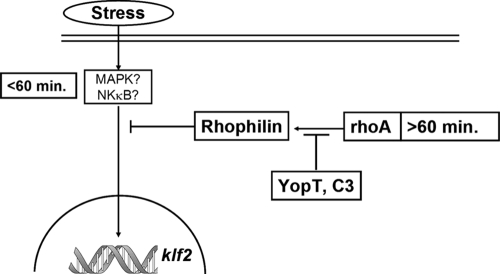
FIG. 6.
Proposed model of klf2 regulation in the context of bacterial infection. Immediately after bacterial contact, host cells induce klf2 by an as yet uncharacterized signaling cascade; however, MAPK or NF-κB signaling may be involved. Two hours after infection, signaling via RhoA and rhophilin 1 suppresses klf2 expression. Bacteria mediate long-term expression of klf2 by suppressing this inhibitory action of RhoA via Rho-inactivating enzymes.