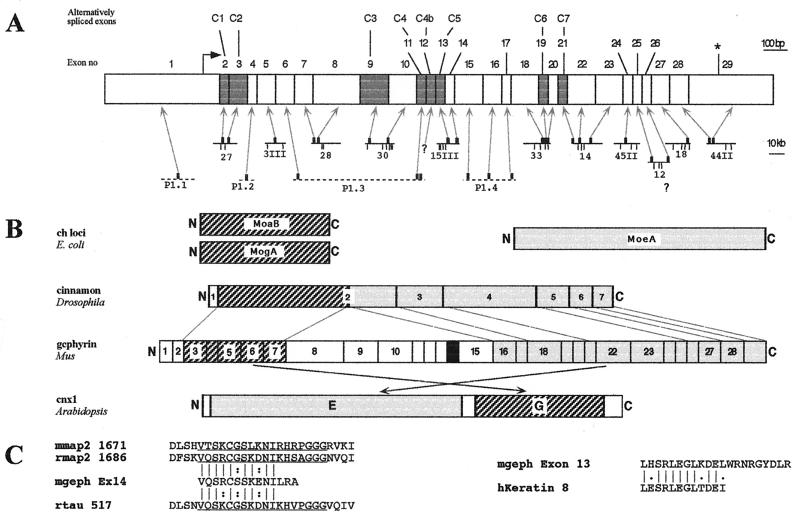
Figure 2.
Structure of the murine gephyrin gene and domain analysis of the encoded protein. (A) Exon positions and relevant restriction sites of murine gephyrin genomic DNAs. (Upper) The exon borders of the gephyrin gene are projected onto a schematic representation of the gephyrin cDNA. An arrow marks the initiation codon, an asterisk the stop signal. Gray boxes indicate the alternatively spliced exons C1–C7. (Lower) Positions and lengths of genomic clones. Arrows indicate the relative positions of the exonic sequences on the isolated λ phages (solid lines) and P1 clones (dashed lines). Clone numbers and EcoRI restriction sites (vertical bars) used for mapping are indicated. Note different scales of size bars for both representations. (B) Comparison of the exon-intron boundaries and domains of gephyrin with sequence similarities to bacterial, invertebrate, and plant Moco proteins. Boxes and numbers within cinnamon and gephyrin correspond to the exons of the respective genes. Dashed and gray boxes indicate regions with sequence similarities to the bacterial proteins MoaB/MogA and MoeA, respectively. The black box in the central region of gephyrin indicates the region displaying sequence similarity to microtubule associated proteins encoded by exon 14. Dashed lines mark exon/intron boundaries conserved between cinnamon and gephyrin. Crossed arrows indicate swapping of the MoaB/MogA and MoeA homology domains in cnx 1 as compared with cinnamon and gephyrin. (C) Alignment of the amino acid motifs encoded by exons 13 and 14 of the murine gephyrin gene with the core repeat motif of MAP2 and tau and the oligomerization domain of keratin 1B. The motif encoded by exon 14 aligns well with the second imperfect octadecapeptide repeat of the microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 from mouse (mmap2), MAP2 from rat (rmap2) and tau from rat (rtau) and the C-terminal sequence predicted from exon 13 aligns well with the oligomerization domain of keratin 1B. Identical residues are indicated by dashes, and isofunctional ones by two dots.