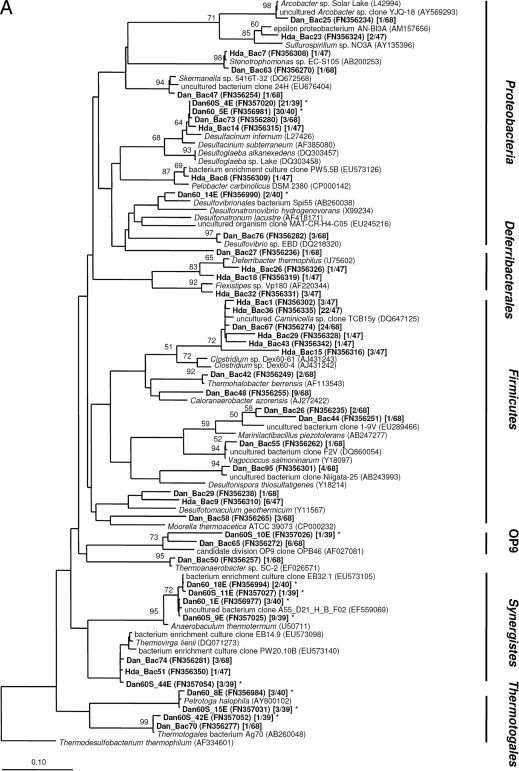
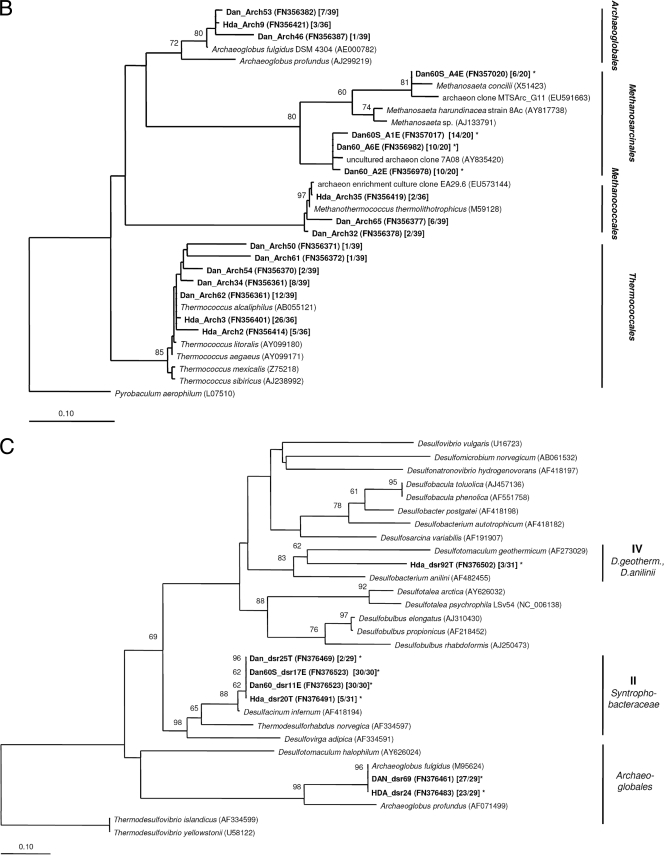
FIG. 2.
Neighbor-joining distance trees showing the phylogenetic relationship of bacterial (A) and archaeal (B) 16S rRNA gene sequences and deduced DsrAB amino acid sequences (C) of representative clones derived from PW samples and enrichment cultures (all shown in bold). Sequences from this study are named according to the sampling sites (Dan and Halfdan [Hda]) and the enrichment conditions (Dan60 and Dan60S). Accession numbers are given in parentheses. Square brackets show the number of sequences out of the total number of sequences analyzed. 16S rRNA-based trees were constructed using either the Bacteria or the Archaea filter of the ssu_jan04_corr_optARB database (http://www.arb-home.de). Short sequences (16S rRNA, <1,300 nt; DsrAB, <540 amino acids), marked by asterisks, were added without changing the overall tree topology using maximum parsimony criteria. DsrAB gene group names refer to those used by Kaneko et al. (23). Bootstrap values are based on 1,000 replicates; only values greater 50% are indicated near the nodes. The scale bar represents 10% sequence divergence.