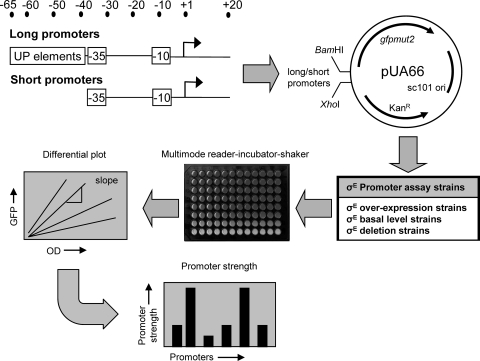
FIG. 1.
Methodology for measuring the strength of σE-dependent promoters. For 60 σE-dependent promoters, short fragments containing the core −35/−10 elements (−35 to +20) and long fragments that also included the UP element (−65 to +20) were cloned into the GFP expression vector pUA66. These promoter plasmid libraries were transformed into assay strains that either overexpressed σE (derivatives of CAG58200), contained basal levels of σE (derivatives of CAG45113 and CAG55907), or with σE deleted (derivatives of CAG22216 [contains a suppressor of σE essentiality]). Strains were grown in 96-well plates at 32°C with aeration (shaking) in a multimode Varioskan. Cell growth (optical density) and GFP fluorescence (RFU) were measured every 15 min. For each strain, differential plots were constructed of GFP fluorescence versus cell growth. Promoter strength was calculated from the slope of the linear portions of the plot, corresponding to the exponential or stationary growth phase. All calculated promoter strengths were subtracted for background culture and medium fluorescence by using control assay strains carrying the promoterless GFP vector pUA66. See Materials and Methods for further details.