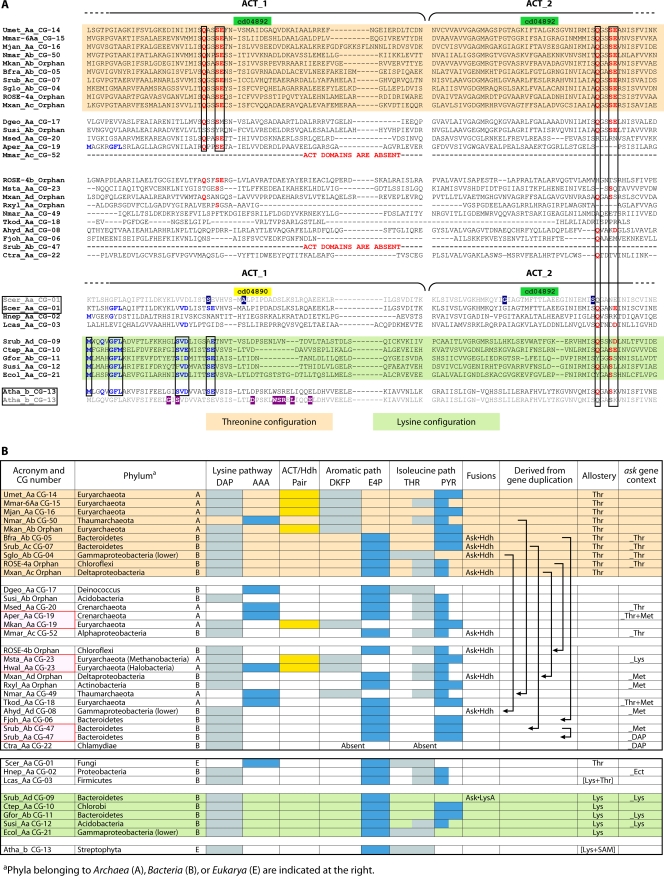
FIG. 8.
Overall features of regulation within the ASKα subhomology division. (A) Alignment of the Q…Q region of the ACT_1-ACT_2 regulatory domains. This region corresponds to the nonequivalent threonine-binding sites described by Paris et al. (71). A cd04892-cd04892 organization is associated with regulation by threonine. At the top, the 10 cohesion groups and orphans exhibiting perfect QXXSE…QXXSE threonine configuration presumably possess a threonine-inhibited Ask and a threonine-inhibited Hdh, as suggested at the right of panel B in the corresponding section. The next block of four possess a recognizable threonine configuration, but with disruption of the motif. The CG-52 Ask enzymes lack the ACT domains but are included because the fusion with Hdh and the gene context (panel B) clearly indicate functional specialization for threonine. The next block of 10 have diverged away from threonine specialization, and in most cases, the new specialization can be inferred (see the text). At the bottom, a different cd organization (cd04890-cd04892) is associated with a pattern of lysine regulation. The green-shaded sequences indicate a perfect “lysine configuration” of allostery, based upon X-ray crystal studies (47), and important residues are boxed and shown in blue. Although the four cohesion groups above the lysine configuration are derivatives of it, they have unknown allosteries (CG-02) or different allosteries (CG-01 members are threonine inhibited, CG-03 members are inhibited synergistically by lysine-plus-threonine combinations, and CG-13 members are inhibited synergistically by lysine-plus-SAM combinations). Amino acid residues shown to be important for threonine inhibition of the yeast Scer_Aa Ask (2) are shown with white letters against a blue background on the dimmed line, and amino acid residues shown to be important for SAM binding in Arabidopsis (54) are shown in magenta at the bottom. (B) The same Ask sequences as in panel A are displayed in a context of operation within the total ASK network and the regulatory implications. The presence of one or another of alternative biosynthetic pathways for lysine, aromatic amino acids, and isoleucine are indicated by shaded blocks. Light-blue shading is used for the Ask-relevant alternatives, and dark-blue shading is used for Ask-irrelevant alternatives. The descending arrows indicate the origins of functionally divergent paralogs in the middle section from the putative ancestral threonine-regulated Ask enzymes in the upper section. Srub_Ab in CG-47 was derived by gene duplication and then underwent another gene duplication to produce another paralog (Srub_Aa) in CG-47.