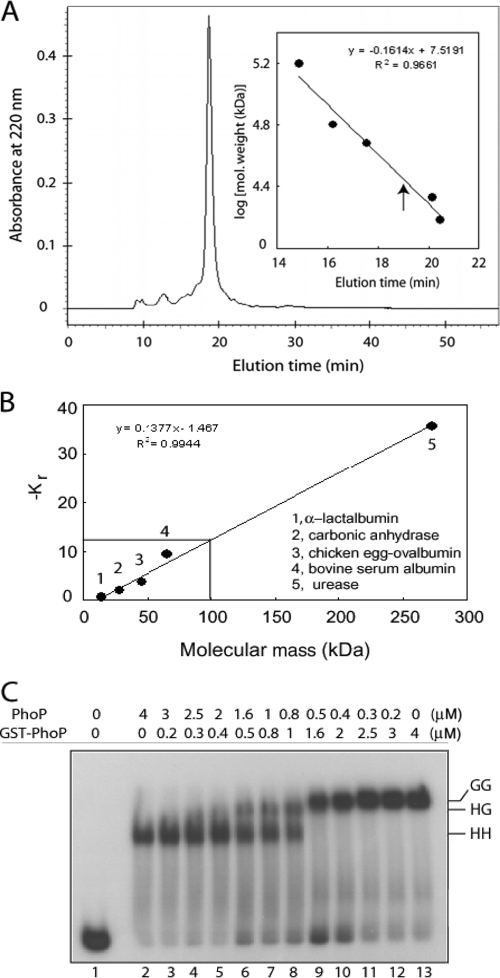
FIG. 4.
Stoichiometry of PhoP-DNA interactions. (A) Gel filtration chromatography was performed with ∼20 μg of purified PhoP. The inset shows a calibration curve of protein standards generated to determine approximate molecular mass of PhoP. Elution time of PhoP is indicated by an upward arrow. (B) PhoP-DNA complexes were resolved on a series of native polyacrylamide gels alongside nondenatured protein molecular mass standards, as described in Materials and methods. The retardation coefficient (Kr) values for protein standards were defined by Ferguson analysis and plotted as a function of molecular mass. Interpolation of −Kr (solid lines) indicated a molecular mass of ∼99.2 kDa for the PhoP-DNA complex. (C) DR1,2 comprising two 9-bp direct repeat motifs in tandem binds two molecules of PhoP. For the competitive EMSA experiment, ∼20 nM end-labeled DR1,2 DNA was incubated in binding reactions with recombinant forms of PhoP. Binding reactions contained no protein (lane 1), 4 μM PhoP alone (lane 2), 4 μM GST-PhoP alone (lane 13), and mixtures of indicated concentrations of PhoP and GST-PhoP (lanes 3 to 12). Protein-DNA complexes were analyzed as described for Fig. 1. HH, two molecules of PhoP; GG, two molecules of GST-PhoP; HG, one molecule each of PhoP and GST-PhoP bound to end-labeled DR1,2.