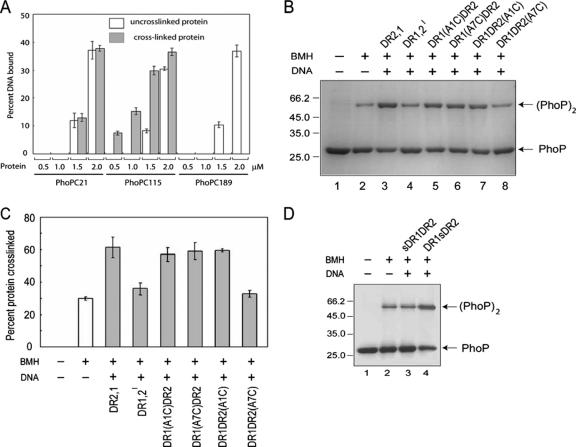
FIG. 6.
PhoP binds head-to-head to DNA. (A) Effect of BMH cross-linking of single cysteine mutants of PhoP on DNA-binding compares percent DR1,2 DNA bound of non-cross-linked (empty columns) and BMH cross-linked (filled columns) proteins at the indicated protein concentrations. (B) Relative efficiency of cross-linking (∼7.5 μM) of PhoPC115 in the absence or presence of the indicated DNA substrates. Above the figure, the absence or presence of BMH and various oligonucleotide based DNA probes (see Materials and Methods for details) is indicated by “−” or “+,” respectively. The sizes of the molecular mass markers, along with the non-cross-linked and cross-linked PhoPs, are indicated as for Fig. 5. (C) BMH cross-linking in the absence or presence of the indicated oligonucleotides was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and quantified by densitometric analysis, and the percent protein cross-linking is shown. (D) Relative ability of ∼7.5 μM PhoPC115 to form BMH cross-linked dimers in absence or presence of the indicated DNA substrates (sDR1DR2 and DR1sDR2). The absence or presence of BMH and DNA substrates are as described for Fig. 5. (C) The sizes of the molecular mass markers and the non-cross-linked and cross-linked PhoPs are indicated for Fig. 5.