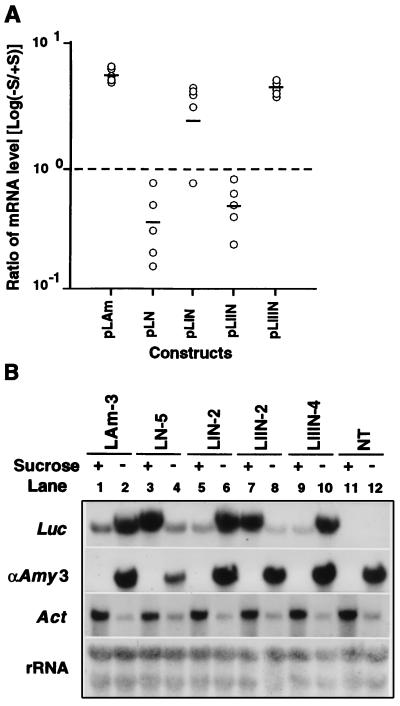
Figure 2.
The αAmy3 3′ UTR and its subdomains independently mediate sugar-dependent repression of heterologous mRNA accumulation in transformed rice suspension cells. Rice suspension cells were transfected with plasmids shown in Fig. 1 and cultured as described in Materials and Methods. Four weeks after transfection, the transformed suspension cells were cultured in sucrose-containing or sucrose-free medium for 2 days and total RNA was purified. (A) Levels of Luc mRNA were analyzed with RNA dot blot analysis by using the Luc coding region as a probe. Radioactive signal representing the amount of Luc mRNA in each dot was quantified by using a PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics). For each construct, the ratio of mRNA level was determined by dividing the level of Luc mRNA in cells starved for sucrose (−S) by that in cells provided with sucrose (+S). Logarithm value of the ratio (open circle) was then used to plot the graph. Bars represent the average value for each construct. (B) Gel blot analysis of mRNA from one representative transformed cell line of each construct. NT indicates nontransformed control. Five micrograms of total RNA was loaded in each lane. The same blot was stripped and rehybridized with indicated probes as described previously (8). The probes were Luc, Act1 (22), and rRNA (23) cDNAs and αAmy3-specific DNA (8). The Luc and αAmy3 probes hybridized to a same blot, and the Act and rRNA probes hybridized to another parallel-prepared blot.