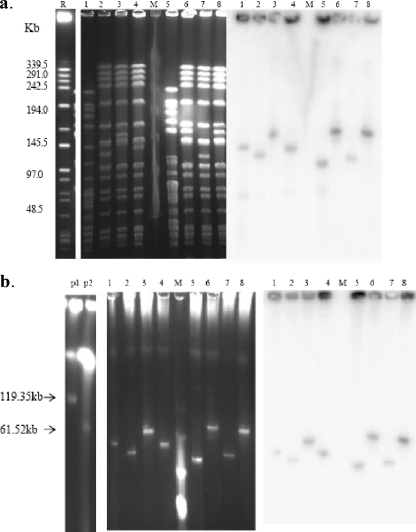
FIG. 2.
(a) PFGE of genomic DNA and hybridization profiles of the vanA gene. (b) Undigested PFGE to identify plasmids and hybridization profiles of the vanA gene. Lanes: R, the recipient strain, E. faecium BM4105RF (Fusr Rifr); 1, E. faecium ZP2298 (clinical VRE isolate); 2, E. faecium FBV2298, which showed teicoplanin-resistant subcolonies present in the clear zone of inhibition; 3, transconjugant E. faecium FB2298 (teicoplanin heteroresistant); 4, FBG2298, strain after three serial passages on the BHI agar without vancomycin from FBV2298; M, lambda ladder; 5, E. faecium ZP2171 (clinical VRE isolate); 6, E. faecium FBV2171, which showed teicoplanin-resistant subcolonies present in the clear zone of inhibition; 7, transconjugant E. faecium FB2171 (teicoplanin heteroresistant); 8, FBG2171, strain after three serial passages on the BHI agar without vancomycin from FBV2171; p1, plasmid R448 (119.35 kb); p2, plasmid R626 (61.52 kb). Preparations were run in 1% agarose under 6.0 V/cm for 22 h with a pulsing time linearly ramped from 3 to 20 s.