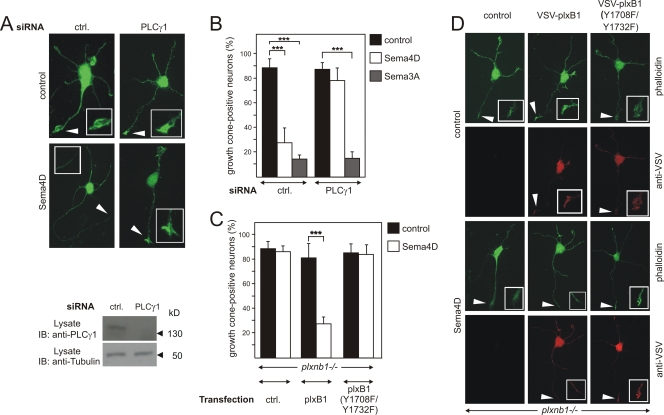
FIG. 9.
Role of PLCγ1 in plexin-B1-mediated growth cone collapse. Primary E17.5 hippocampal neurons from wild-type (A and B) or plexin-B1-deficient embryos (C and D) were transfected with control (ctrl.) siRNA or siRNA against PLCγ1 (A and B) or with vector alone (ctrl.) or vectors carrying wild-type VSV-plexin-B1 or its mutant, [VSV-plxB1(Y1708F/Y1732F)]. At 48 h later, cells were incubated without (control) or with 150 nM Sema4D or 2 nM Sema3A. Knockdown of PLCγ1 was verified by immunoblotting of cell lysates with an anti-PLCγ1 antibody. Shown are representative hippocampal neurons incubated without or with Sema4D and stained with phalloidin-FITC (A and D) and counterstained with an anti-VSV antibody (D) to identify transfected cells. Insets show a magnified view of axonal ends or growth cones, which are indicated by arrows. (B) Hippocampal neurons were scored for growth cone collapse after treatment with control medium, 150 nM Sema4D, or 2 nM Sema3A. (C) Transfected neurons, identified by immunocytochemistry using anti-VSV antibodies, were scored for growth cone collapse. Shown are mean values of three independent experiments (n = 300; ± standard errors of the means). ***, P ≤ 0.001.