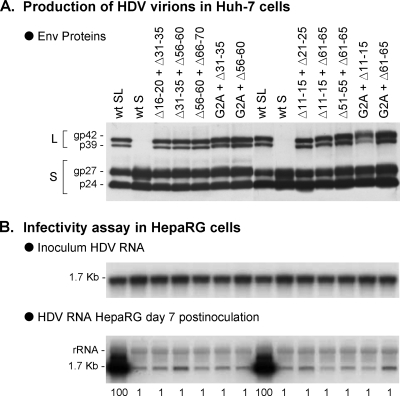
FIG. 2.
Relative infectivity of HDV particles bearing two distinct infectivity-deficient pre-S1 mutants. SL-HDV particles bearing wt S-HBsAg proteins and two distinct infectivity-deficient L-HBsAg proteins in equivalent proportions were produced in Huh-7 cells. Infectivity-deficient L-HBsAg proteins included G2A, a protein lacking a myristoylation signal, and proteins with small deletions in the 2-to-48 (Δ11-15, Δ16-20, Δ21-25, and Δ31-35) or the 49-to-75 pre-S1 sequence (Δ51-55, Δ56-60, Δ61-65, and Δ66-70). (A) Particles from 0.5 ml of cell culture supernatant were analyzed for S- and L-HBsAg proteins by immunoblotting. The glycosylated (gp) and nonglycosylated (p) forms of S- and L-HBsAg are indicated. (B) Genomic HDV RNA from 140 μl of supernatant was analyzed by Northern blotting. After normalization of the different preparations of HDV virions for their HDV RNA content, they were assayed for infectivity in cultures of HepaRG cells. Infectivity was evaluated by measuring the accumulation of HDV RNA in cells harvested at day 7 postinoculation. Quantification of HDV RNA signals by phosphorimager is indicated as percentages of the value for wt SL-HDV. The experiment was repeated with consistent results.