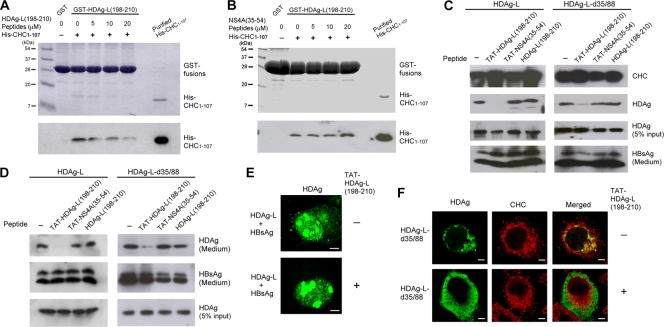
FIG. 5.
Effect of the cell-permeable peptide TAT-HDAg-L(198-210) on the nuclear transport of HDAg-L and the assembly of HDV. (A and B) Competition of HDAg-L(198-210) peptide with GST-HDAg-L(198-210) for interacting with His-CHC1-107. GST pulldown competition assay was performed with GST-HDAg-L(198-210), purified His-CHC1-107, and various amounts of HDAg-L(198-210) peptide (A) or NS4A(35-54) peptide (B) as indicated. Coomassie blue staining (top) and Western blot analysis with antibodies against the His tag of CHC1-107 (bottom) are shown. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left of the blots. (C and D) Effects of TAT-HDAg-L(198-210) peptide on the interaction of HDAg-L with CHC and the assembly of HDV. COS7 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding small HBsAg and HDAg-L or HDAg-L-d35/88. Eight hours posttransfection, the cell-permeable peptides TAT-HDAg-L(198-210) and TAT-NS4A(35-54) and the nonpermeable control peptide HDAg-L(198-210) as indicated were added at a concentration of 20 μg/ml into the culture medium. Cells harvested 2 days posttransfection and VLPs collected 4 days posttransfection were subjected to analysis as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (E and F) Effects of TAT-HDAg-L(198-210) peptide on the subcellular distribution of HDAgs. COS7 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding HDAg-L and small HBsAg (E) or transfected with plasmid encoding HDAg-L-d35/88 (F). Eight hours posttransfection, cells were incubated with TAT-HDAg-L(198-210) peptide (+) at a concentration of 20 μg/ml for 40 h, followed by immunofluorescence staining with antibodies against HDAg or CHC as indicated.