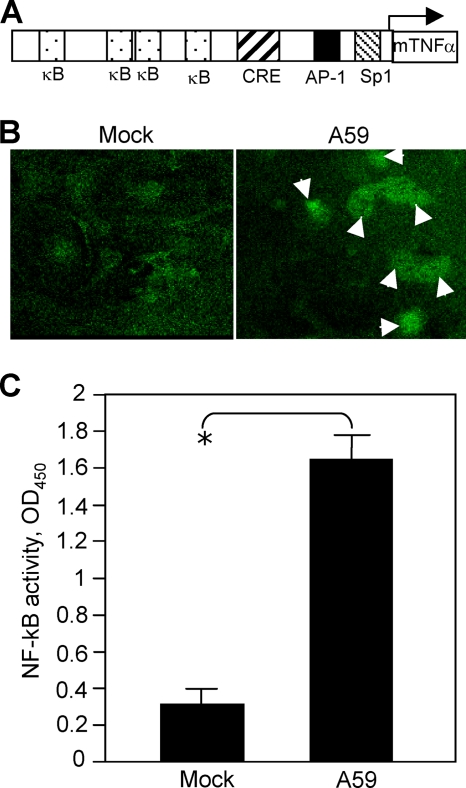
FIG. 7.
Activation of TNF-α by MHV-A59 infection. (A) Schematic diagram showing the sequence elements of the murine TNF-α (mTNF-α) promoter and the binding sites for transcription factors NF-κB (κB), CRE, AP-1, and Sp1. (B) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB following MHV-A59 infection. Cells were infected with MHV-A59 at an MOI of 5 for 18 h (right) or mock infected (left). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with primary anti-NF-κB p65 polyclonal antibody and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody. The images were taken with a digital camera under a fluorescence microscope. The arrows indicate the nuclear translocation. (C) Assay for NF-κB activation. Primary astrocytes were infected with MHV-A59 at an MOI of 5 or mock infected. At 18 h p.i., nuclear extracts were isolated and NF-κB activity was determined with the TransAM NF-κB p65 kit as described in Materials and Methods. The results are expressed as the mean absorbance at 450 nm (OD450) for three independent experiments. The error bars indicate standard deviations of the mean. The asterisk indicates statistical significance between the pair (P < 0.05).