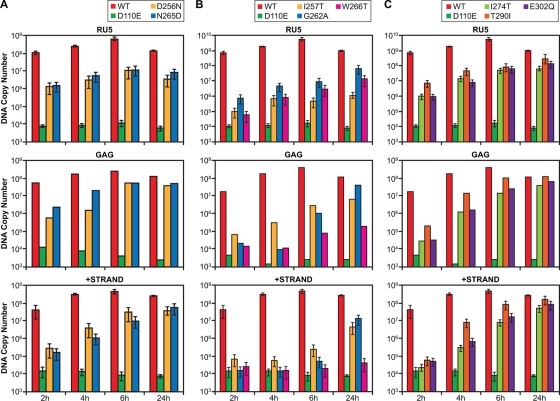
FIG. 1.
Viral DNA synthesis. Real-time PCR was used to measure the amounts of viral DNA at various times for three important stages of viral DNA synthesis: the probes were designed to measure the amount of viral DNA made early (RU5), near the completion of minus-strand synthesis (Gag) and at the second transfer between templates (plus-strand transfer). Mutants that were analyzed at the same time are shown together. (A) Levels of viral DNA present at various times after infections with the D256N and N265D mutants. (B) Levels of viral DNA present at various times after infections with the I257T, G262A, and W266T. (C) Levels of viral DNA present at various times after infections with the I274T, T290I, and E302Q mutants. The plus-strand transfer and RU5 experiments were done at least twice, while the Gag experiments were done once.