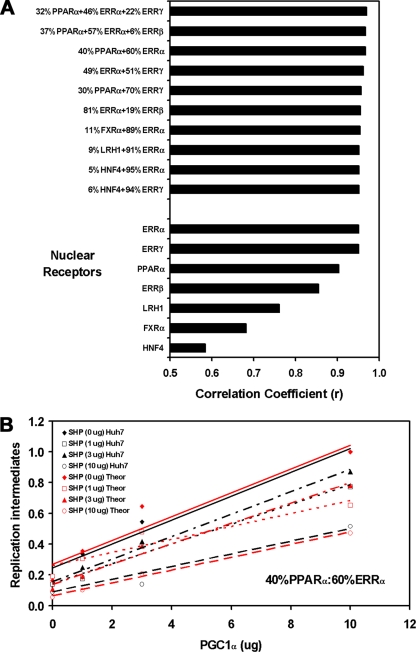
FIG. 7.
Theoretical evaluation of the nuclear receptor combinations governing HBV biosynthesis in Huh7 cells. (A) Correlation coefficients were determined for optimal combinations of nuclear receptors based on their effects on viral replication in 293T cells compared with that in Huh7 cells in the presence of the different levels of the PGC1α and SHP coregulators. The combinations of nuclear receptors are reported in a descending order, with respect to their correlation coefficient values. Data used to determine the correlation coefficient values for RXRα/FXRα and LRH1 are included in the companion study (27a). 32% RXRα/PPARα plus 46% ERRα plus 22% ERRγ, r = 0.969; 37% RXRα/PPARα plus 57% ERRα plus 6% ERRβ, r = 0.968; 40% RXRα/PPARα plus 60% ERRα, r = 0.967; 49% ERRα plus 51% ERRγ, r = 0.962; 30% RXRα/PPARα plus 70% ERRγ, r = 0.957; 81% ERRα plus 19% ERRβ, r = 0.955; 11% RXRα/FXRα plus 89% ERRα, r = 0.954; 9% LRH1 plus 91% ERRα, r = 0.952; 5% HNF4α plus 95% ERRα, r = 0.952; 6% HNF4α plus 94% ERRγ, r = 0.952; 100% ERRα, r = 0.951; 100% ERRγ, r = 0.950; 100% RXRα/PPARα, r = 0.903; 100% ERRβ, r = 0.855; 100% LRH1, r = 0.761; 100% RXRα/FXRα, r = 0.682; 100% HNF4α, r = 0.585. (B) Example of the theoretical optimal best fit of the levels of viral replication obtained with RXRα/PPARα plus ERRα in 293T compared with that in Huh7 cells in the presence of the different levels of the PGC1α and SHP coregulators. Trend lines were calculated using linear regression analysis.