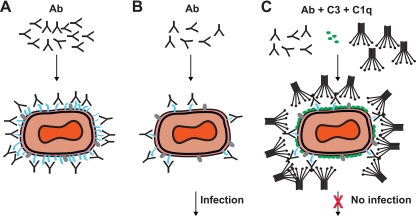
FIG. 10.
Model of VACV EV neutralization. Schematic diagrams of potential virion neutralization pathways. B5 is drawn in blue. Another representative EV surface antigen is drawn in gray. Ab, anti-B5 antibody. (A) Basic occupancy model. Antibodies against B5 could completely coat the virion surface and thereby neutralize the virus. This model failed. (B) Model 2. VACV EV escape neutralization by anti-B5 antibody binding due to low density of the B5 protein on the surface of EV. Direct occupancy of B5 with anti-B5 IgG is insufficient to block infection of target cells. (C) Complement-assisted coating of VACV EV (opsonization). Antibody-mediated protection against VACV EV is dependent on antibody recruitment of complement C1q and covalent attachment of C3 to the surface of the virus. See Discussion for details.