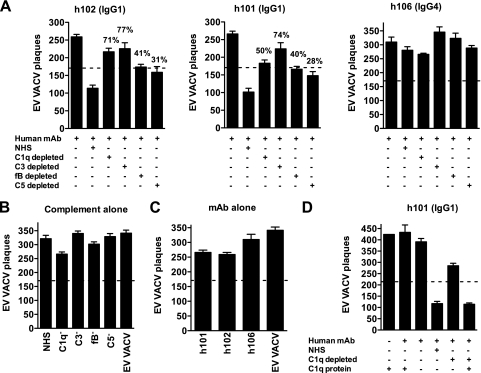
FIG. 6.
. Complement activation pathways. (A to C) VACV EV neutralization by the anti-B5 MAb at 10 μg/ml (h101 IgG1, h102 IgG1, or h106 IgG4 isotype) in the presence of human complement (NHS) or C1q-, C3-, fB- or C5-depleted human sera (10%). The dashed line indicates 50% neutralization based on that for VACV EV alone without antibody and complement. Significant decreases in anti-B5 MAb (h101 or h102 IgG1 isotype) VACV EV neutralization were observed when the complement component C1q, C3, C5, or fB was depleted. Percent EV neutralization activity loss in the absence of C1q or C3 was higher than that in the absence of fB or C5. (B) EV neutralization by human complement (NHS) or C1q-, C3-, fB-, or C5-depleted sera alone. (C) Anti-B5 MAb h101 IgG1, h102 IgG1, or h106 IgG4 neutralization in the absence of complement. (D) EV neutralization by anti-B5 MAb (h101 IgG1) at 10 μg/ml in the presence of human complement (NHS), C1q-depleted sera, or C1q-purified protein. The addition of the C1q protein (10 μg/ml) to C1q-depleted sera restored EV neutralization activity. Data are representative of three experiments. Error bars indicate the SEM in each group.