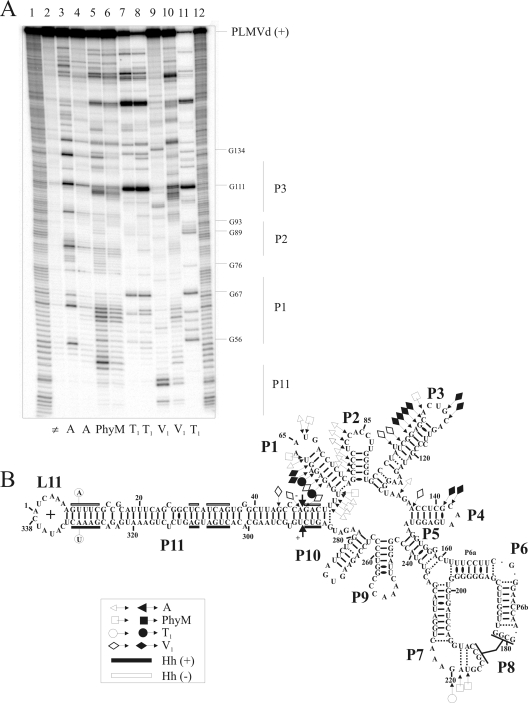
FIG. 6.
Enzymatic probing of PLMVd with ribonucleases in either the presence or the absence of eEF1A. (A) Typical autoradiogram of an 8% PAGE gel used for analysis of probing performed with a 5′-end-labeled PLMVd strand of (+) polarity. Lanes 1 and 12, identical ladders obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of PLMVd strands; lane 2, nonhydrolyzed RNA sample. The remaining lanes contained RNA samples that were hydrolyzed by RNase A (lanes 3 and 4), RNase PhyM (lanes 5 and 6), RNase T1 (lanes 7 and 8), and RNase V1 (lanes 9 and 10) in either the absence (lanes 3, 5, 7, and 9) or the presence (lanes 4, 6, 8, and 10) of eEF1A. Lane 11 contains PLMVd strands hydrolyzed by RNase T1 at 65°C in order to provide a guanosine ladder. (B) Compilation of mapping differences resulting from the addition of eEF1A on the model secondary structure of the PLMVd (+) strand. Opened and closed symbols indicate a decrease and increase in the susceptibility to a given RNase, respectively. The legend in the figure shows the symbols used to indicate cleavage by the various RNases (▵, RNase A; □, RNase PhyM; ○, RNase T1; and ⋄, RNase V1). The two mutated nucleotides preventing self-cleavage are circled on the left-hand extremity of the P11 stem. The black and white boxes indicate the conserved nucleotides for both (+) and (−) hammerhead sequences, respectively.