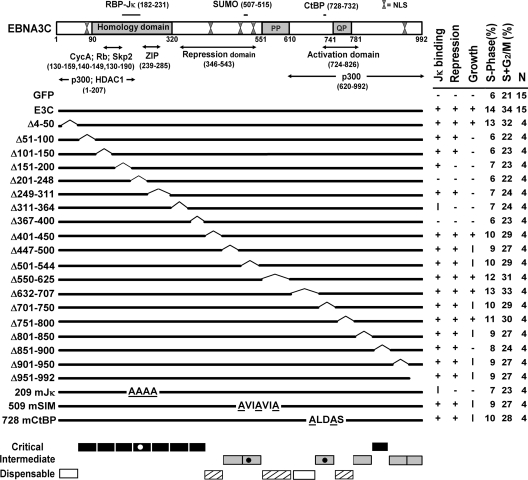
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of EBNA3C domains and mutants with summarized reverse genetic and biochemical data. Within the homology domain (aa 90 to 320), which has the highest level of identity (23 to 30%) among the EBNA3 proteins, aa T209FGC212 are critical for RBP-Jκ association. SUMO-1 and SUMO-3 interaction require D509VIEVID515, and P728LDLS732 mediates CtBP binding. Proline-rich (PP; aa 551 to 610) and glutamine-proline-rich (QP; aa 741 to 781) domains are indicated. Repression (aa 346 to 543) and activation (aa 724 to 826) domains were defined based on their effects when targeted to promoters by fusion to the Gal4 DNA binding domain. Putative leucine zipper (ZIP) and multiple functional nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequences are indicated. The results of wt EBNA3C (E3C) or mutant EBNA3C association with RBP-Jκ, repression of EBNA2 transcriptional activation of the Cp promoter, cell cycle distribution at day 14, and effects on LCL growth under EBNA3C-HT inactivation condition are shown in columns on the right side of the figure. +, wt; −, null; I, intermediate; N, number of complementation experiments. The regions of EBNA3C which are critical (black bars), intermediate (gray bars), and nearly (hashed bars) or completely (white bars) dispensable for LCL growth are indicated at the bottom.