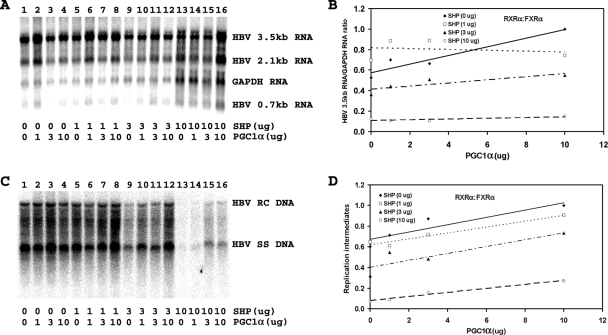
FIG. 2.
Effect of PGC1α and SHP expression on HBV biosynthesis in the human embryonic kidney cell line 293T expressing RXRα/FXRα. Cells were transfected with the HBV DNA (4.1-kbp) construct plus the RXRα and FXRα expression vectors (lane 1) or the HBV DNA (4.1-kbp) construct plus the RXRα, FXRα, PGC1α, and SHP expression vectors (lanes 2 to 16), as indicated. (A) RNA (Northern) filter hybridization analysis of HBV transcripts. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) transcript was used as an internal control for RNA loading per lane. (B) Quantitative analysis of the 3.5-kb HBV RNA results from three independent experiments. Trend lines were calculated using linear regression analysis. (C) DNA (Southern) filter hybridization analysis of HBV replication intermediates. HBV RC DNA, HBV relaxed circular DNA; HBV SS DNA, HBV single-stranded DNA. (D) Quantitative analysis of the HBV replication intermediate results from three independent experiments. Trend lines were calculated using linear regression analysis. All-trans-retinoic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid at 1 μM and 100 μM, respectively, were used to activate the nuclear receptors RXRα and FXRα.