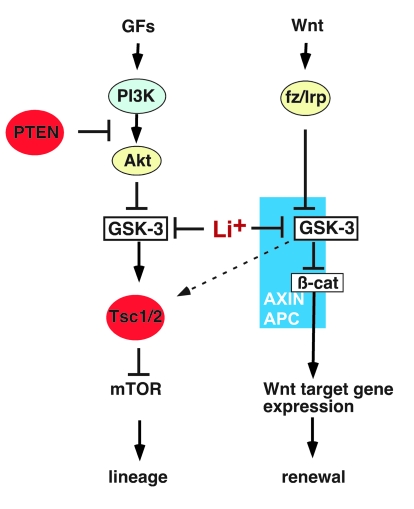
Figure 8. GSK-3 functions in 2 major pathways to regulate HSC self renewal and lineage commitment.
Inhibition of GSK-3 activates Wnt and mTOR signaling. In the canonical Wnt pathway, GSK-3 and β-catenin bind to the Axin complex, along with APC. GSK-3 phosphorylates β-catenin, targeting it for rapid destruction. Wnt binding to the Fz/Lrp receptor complex causes inhibition of GSK-3, which in turn stabilizes β-catenin and activates Wnt target genes that promote progenitor proliferation and self renewal. In PI3K/PTEN-regulated pathways, growth factors (GFs) bind to surface receptors and activate PI3K, leading to activation of Akt, whereas PTEN inhibits activation of Akt. Once activated, Akt phosphorylates and inhibits GSK-3. GSK-3 phosphorylates Tsc2, inhibiting the mTOR pathway. Thus, inhibition of GSK-3 activates mTOR and promotes proliferation and exit from the LT-HSC pool. Inhibition of GSK-3 thus activates distinct downstream signaling pathways that have opposing functions in HSC renewal and differentiation.