Fig. 1.
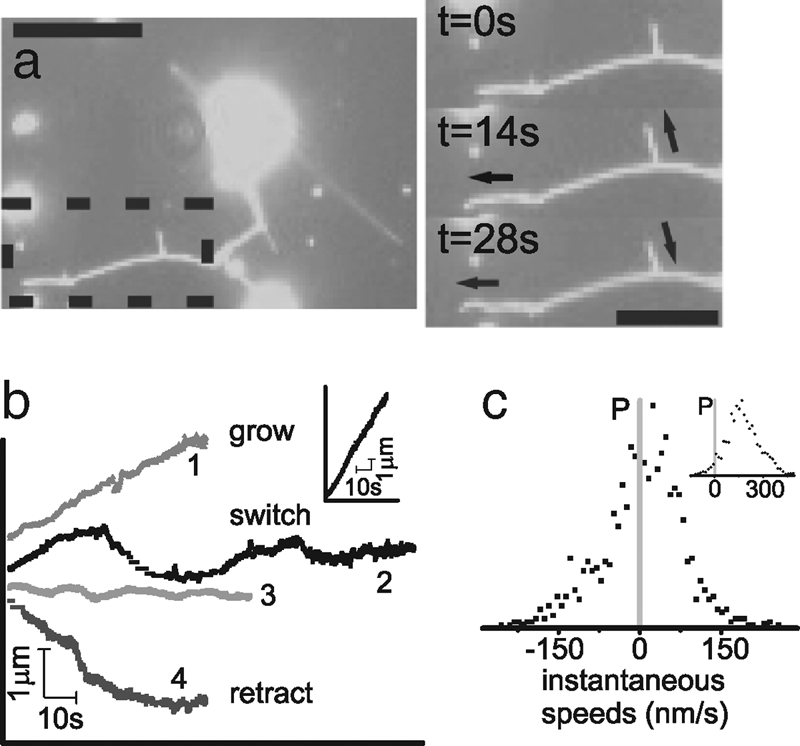
Membrane tubes formed by nonprocessive motors. (a) Fluorescence image of a membrane tube network extracted from GUVs by nonprocessive motors walking on MTs on the underlying surface. The time sequence images on the right show the detailed evolution of the network section within the dashed region on the left. The entire movie is provided as supplementary material. Arrows indicate direction of membrane tube movement: the left arrows indicate a growing tube and the right arrows show a tube that which is switching between growth and retraction (left scale bar, 10 μm; right scale bar, 5 μm). (b) Example traces of membrane tube tips formed by nonprocessive motors as they move in time. There are three distinct behaviors: tube growth (1), tube retraction (4), and switching between growth and retraction (2 and 3), a bidirectional behavior. The behavior is distinctly different for membrane tubes pulled by Kinesin (Inset) where tubes grow at steady high speeds. (c) The distribution of instantaneous tip speeds for membrane tubes pulled by Ncd is asymmetric and centers around zero, with both positive and negative speeds. Kinesin tubes move with only positive speeds (Inset).
