Figure 1.
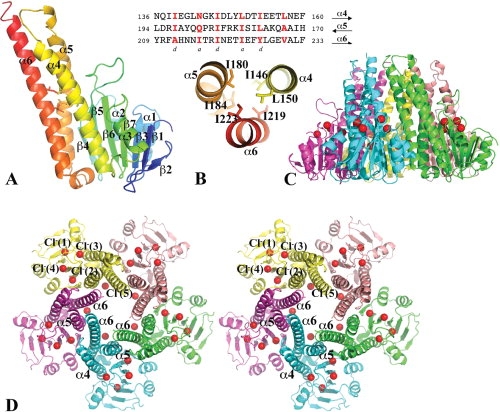
The structure of the Vp-ZntB cytoplasmic domain. (A) A ribbon drawing of the Vp-ZntB cytoplasmic domain monomer structure with the secondary structure in rainbow colors from N- (blue) to C-terminus (red). The subunit can be divided into an N-terminal α/β/α sandwich domain on the right side and a C-terminal coiled-coil like domain on the left side. Six residues [see Fig. 1(B)] contributing to two layers of inter-helical interactions are drawn in stick form. (B) The heptad sequence repeats in the coiled-coil forming helices, α4, α5, and α6. The residues at positions a and d are mostly hydrophobic and form core inter-helical interactions, only two layers of interactions are shown. (C) Ribbon drawings of Vp-ZntB cytoplasmic domain pentamer in the side view. (D) The stereo view of the pentamer from the top. Five monomers are colored differently. The bound Cl− anions, which form a ring, are drawn as red balls. The large opening at the funnel bottom is formed with five α5 helices and five α6 helices. The top small opening is formed by five α6 helices. The second half of the α6 helix interacts with two neighboring α6 helices and one neighboring α6 helix. This interaction seems critical to the formation of the pentamer. Figures 1, 2, and 3 were prepared using the program Pymol (http://www.PyMOL.org).
