Figure 4.
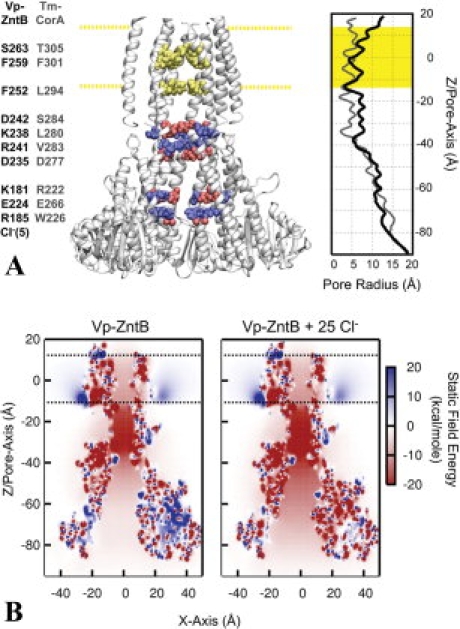
The architecture and static field potential of full-length ZntB. (A) Full-length ZntB, comprised of the crystallographic cytoplasmic domain with a homology modeled transmembrane domain based on Tm-CorA, is shown with one of the monomers removed for a clearer view of the pore. Cytoplasmic residues that contribute significantly to the electrostatic energy of an ion along the central pore are highlighted blue for positively charged residues (R185, K181, K238, and R241) and red for negative [E224, D235, D242, and Cl−(5)]. Residues in the transmembrane domain forming constriction sites are highlighted in yellow (S263, F259, and F252). The corresponding residues of Tm-CorA are listed adjacent to the residues of Vp-ZntB. The membrane is positioned between −12.5 Å < Z < 12.5 Å, as represented by the highlighted yellow regions. The radius profile is shown on the right hand side for the Vp-ZntB and Tm-CorA. (B) Static field potential energy maps of ZntB with and without Cl− ions. The energy of a positive charge in the electrostatic potential produced by the protein charge distribution is shown for every position along the XZ plane of the system. To accentuate the bare static field created by the protein charges and bound Cl− ions, no counter-ion screening was considered inside the pore (i.e., κTM-pore/cyto-pore = 0).
