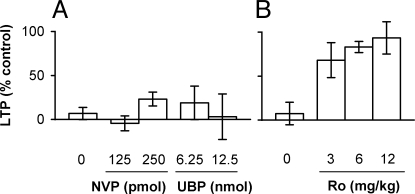
Fig. 2.
Dose-dependence of the effects of subtype-selective NMDAR antagonists on the inhbition of LTP by Aβ1–42. (A) Neither pretreatment with the GluN2A antagonist NVP-AAM077 (125 pmol, n = 5; and 250 pmol, n = 4, i.c.v.) nor the GluN2C/D antagonist UBP141 (6.25, n = 4; and 12.5 pmol, n = 4, i.c.v.) significantly affected the inhibition of LTP by Aβ1–42 (80 pmol, i.c.v., n = 6 for Aβ1–42 alone) (P > 0.05, one-way ANOVA). (B) In contrast, pretreatment with the GluN2B antagonist Ro 25–6981 (3 mg/kg, n = 4; 6 mg/kg, n = 6; and 12 mg/kg, n = 4, i.p.) significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the Aβ1–42-mediated inhibition of LTP (n = 7 for Aβ1–42 alone). LTP values are expressed as the mean (±SEM) % control magnitude of LTP at 3 h after high frequency conditioning stimulation.