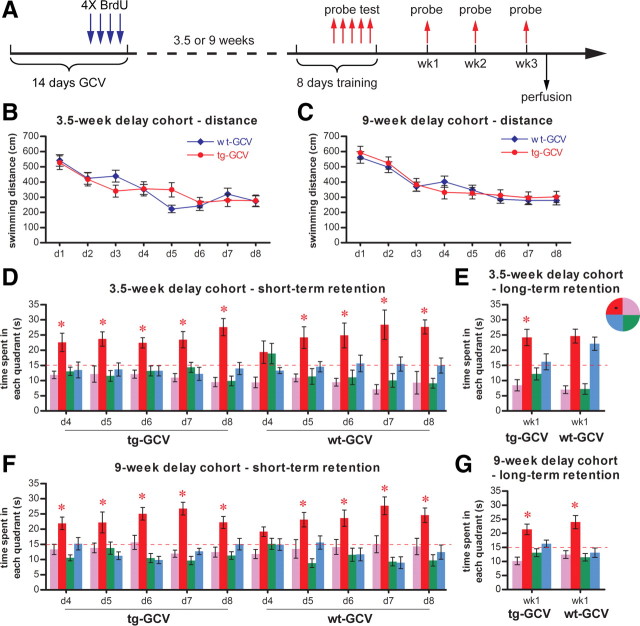
Figure 4.
Learning and memory were not impaired in Nestin-tk mice if training started 3.5 or 9 weeks after GCV treatment. A, The experimental scheme. B, C, Acquisition of the water maze task. GCV-treated transgenic mice in both the 3.5-week-delay cohort (B, ANOVA, F(1,17) = 1.946, p > 0.98, for wt-GCV, n = 9, for tg-GCV, n = 10) and the 9-week-delay cohort (C, ANOVA, F(1,22) = 0.036, p > 0.85, for wt-GCV, n = 13, for tg-GCV, n = 11) performed similarly to wild-type littermate controls, as indicated by distance moved in the maze. D, Short-term retention from daily probe tests from day 4 to day 8 was similar in GCV-treated transgenic mice and wild-type littermates in the 3.5-week-delay cohort. E, Long-term retention in the probe test 1 week after training was similar in GCV-treated transgenic mice and wild-type littermates in the 3.5-week-delay cohort. F, Short-term retention from daily probe tests from day 4 to day 8 was similar in GCV-treated transgenic mice and wild-type littermates in the 9-week-delay cohort. G, Long-term retention in the probe test 1 week after training was similar in GCV-treated transgenic mice and wild-type littermates in the 9-week-delay cohort. The red dotted line indicates chance level (15 s). The hidden platform (black square) is located in the northwest quadrant. *Statistically significant difference between the target quadrant and all other quadrants. For detailed statistical analysis for D–G, see supplemental Table 2, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material. Error bars represent ± SEM.