Figure 5.
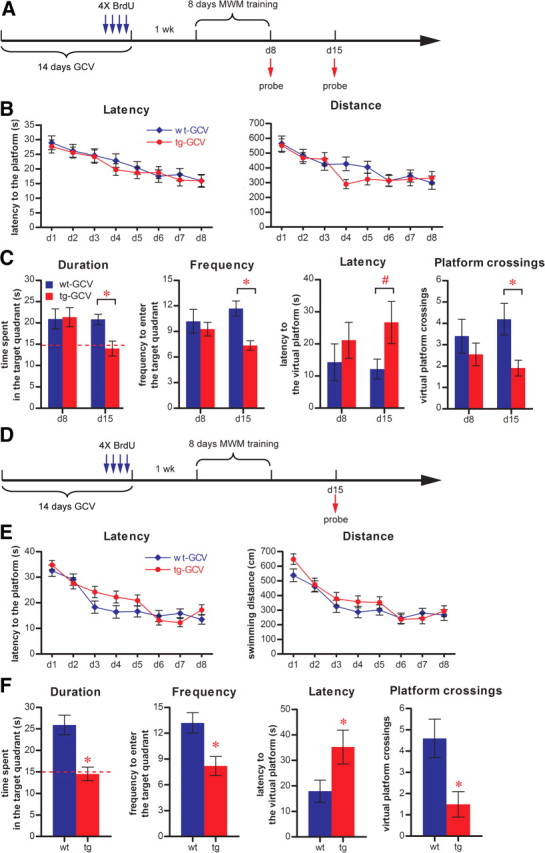
Impaired long-term retention in GCV-treated Nestin-tk transgenic mice. A, The experimental scheme for B and C. B, Neither latency nor distance swum to reach the hidden platform during training was significantly different between tg-GCV and wt-GCV (latency: ANOVA, F(1,19) = 0.184, p > 0.67; distance: ANOVA, F(1,19) = 0.525, p > 0.47; for tg-GCV, n = 11, for wt-GCV, n = 10). C, GCV-treated transgenic mice were defective in long-term retention on day 15 but not in short-term retention on day 8, as indicated by duration in the target quadrant (duration), frequency of entering the target quadrant (frequency), latency to reach the virtual platform (latency), and frequency of entering the virtual platform (platform crossings) (duration: on day 8, F(1,19) = 0.018, p > 0.89, on day 15, F(1,19) = 10.015, p < 0.0051; frequency: on day 8, F(1,19) = 0.345, p > 0.56, on day 15, F(1,19) = 18.232, p < 0.0004; latency: on day 8, F(1,19) = 0.728, p > 0.40, on day 15, F(1,19) = 0.404, p > 0.067; platform crossings: on day 8, F(1,19) = 0.834, p > 0.37, on day 15, F(1,19) = 8.097, p < 0.0103). D, The experimental scheme for E and F. E, Neither latency nor distance swum to reach the hidden platform during training was significantly different between tg-GCV and wt-GCV (latency: ANOVA, F(1,19) = 0.604, p > 0.44; distance: ANOVA, F(1,19) = 1.077, p > 0.31; for tg-GCV, n = 11, for wt-GCV, n = 10). F, GCV-treated transgenic mice were defective in long-term retention as indicated by duration (t(19) = 4.170, p < 0.0005), frequency (t(19) = 3.184, p < 0.0049), latency (t(19) = 2.142, p < 0.0454), and platform crossings (t(19) = 2.917, p < 0.0088). The red dotted line indicates chance level (15 s). *Statistically significant difference; #nonsignificant increase of latency in tg-GCV. Error bars represent ± SEM.
