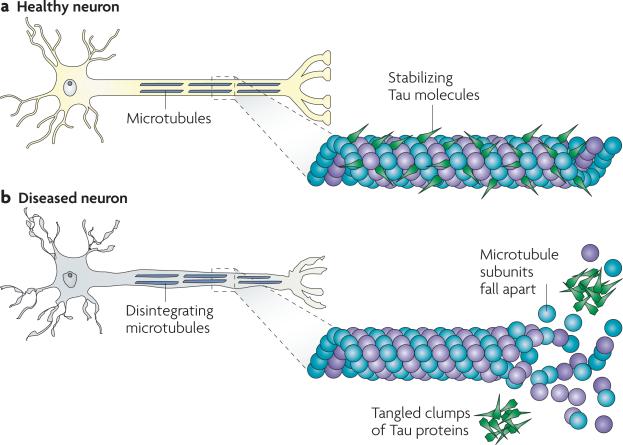
Figure 2. Tau in healthy neurons and in tauopathies.
Tau facilitates microtubule (MT) stabilization within cells and it is particularly enriched in neurons. MTs serve as “tracks” that are essential for normal trafficking of cellular cargo along the lengthy axonal projections of neurons, and it is thought that tau function is compromised in Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. This probably results both from tau hyperphosphorylation, which reduces the binding of tau to MTs, and through the sequestration of hyperphosphorylated tau into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) so that there is less tau to bind MTs. The loss of tau function leads to MT instability and reduced axonal transport, which could contribute to neuropathology.