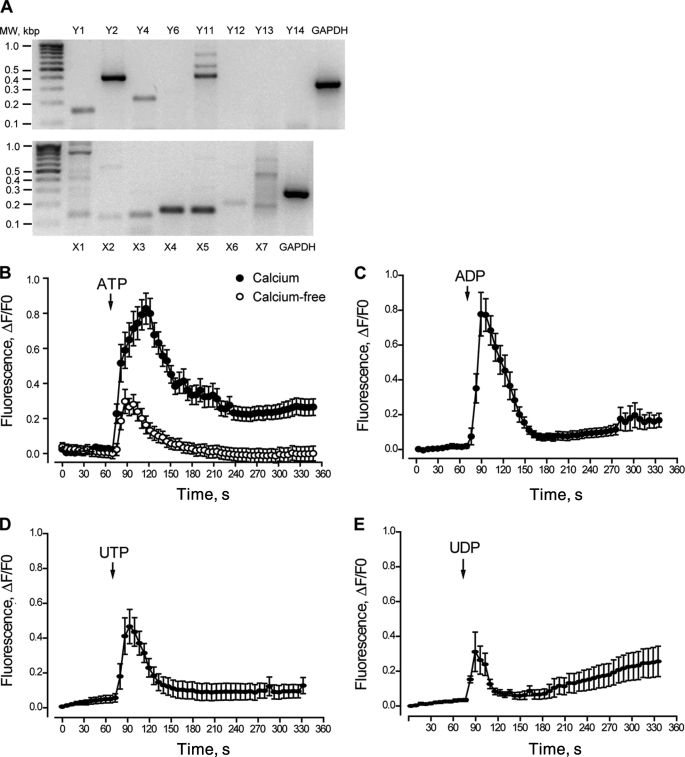
FIGURE 1.
Molecular and pharmacological determination of P2Y/P2X receptors in rat skeletal myotubes. A, mRNA for several P2Y and P2X receptor subtypes is expressed in skeletal myotubes derived from newborn rat primary cultures. Total RNA was extracted from differentiated skeletal myotubes, and the mRNA for all the P2X/P2Y receptor subtypes was assessed by RT-PCR and detected in 1.5% agarose gels on the basis of their estimated molecular weight. A representative gel of three different RNA extractions is presented. B–E, natural agonists for P2Y/P2X receptors evoke calcium transients in skeletal myotubes. The effect of ATP, ADP, UTP and UDP (500 μm) over intracellular calcium changes was assessed in skeletal myotubes. A sequence of images was taken with the charge-coupled device camera attached to the epifluorescence microscope side port, which was equipped with the correct filters to capture fluo3-AM fluorescence to monitor the intracellular Ca+2 level. The analyzed regions of interest were from whole myotubes, considering both cytosolic and nuclear components. Stimuli were applied where indicated by an arrow and maintained throughout the recording period. Traces correspond to mean ± S.E. For each condition, 20–50 cells coming from 4–10 independent coverslips were quantified. In B, ATP was assessed either in regular Krebs buffer (solid circles, 1 mm Ca+2) or in calcium-free Krebs buffer (open circles, 0 Ca+2 plus 2 mm EGTA). All other nucleotides were assessed in regular Krebs buffer.