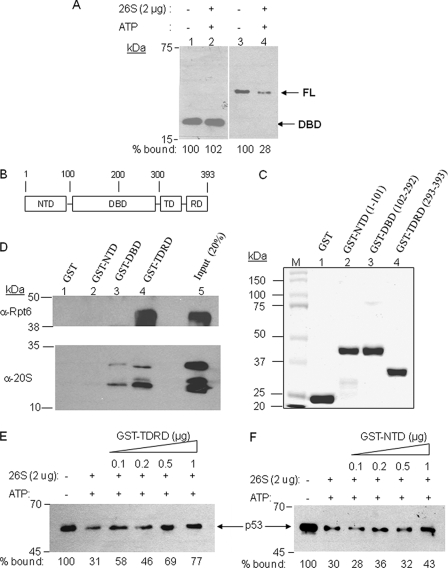
FIGURE 4.
Identification of the p53 domain responsible for physical and functional interaction with the 19 S proteasome. A, the destabilization assay was carried out as described in Fig. 1 using either the isolated DNA-binding domain or full-length p53. B, domain map of p53. C, purification of GST-fused recombinant proteins of p53 domains. Each of the three domains, N-terminal domain (NTD), DNA-binding domain (DBD), and C-terminal tetramerization and regulatory domain (TDRD) and the number of amino acids are indicated in the SDS-PAGE of purified proteins. D, Western blots using either anti-Rpt6 or anti-20 S antibodies show the amount of protein retained by the p53 domain indicated after incubation of the GST-p53 domain fusion protein with intact 26 S proteasome. E and F, competition assay to examine the ability of the p53 TDRD (E) and NTD (F) regions to inhibit proteasome-mediated destabilization of immobilized p53·DNA complex. The assay was carried out as described in Fig. 1, except the indicated amounts of the GST fusion proteins were included as competitors for binding to the proteasomal ATPases. The amount of p53 retained on the DNA is shown.