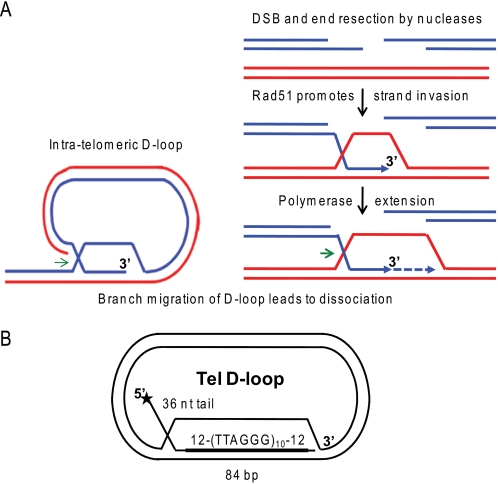
FIGURE 1.
Schematic of D-loops at telomeric ends and in homologous recombination. A, the 3′ ssDNA tails generated at a double strand break by nucleases or present at a collapsed replication fork are coated by Rad51 filaments. Then Rad51 promotes strand invasion and pairing with homologous sequence in duplex DNA. A polymerase can initiate DNA synthesis at the 3′-end of the invading strand. D-loops also exist at telomeric ends, whereby the 3′ tail invades homologous telomeric duplex DNA. Branch migration of the D-loops in the direction of the green arrows mediates D-loop disruption for replication fork progression at the telomeres or for completion of repair as in the synthesis-dependent strand-annealing pathway. B, schematic of 5′-tailed telomeric (Tel) mobile D-loop. The star denotes the 5′-end radiolabel. The invading strand base-pairs with the plasmid to form an 84-bp duplex with 10 TTAGGG repeats flanked by 12 bp of unique sequence with a protruding 5′ 36-nt single strand tail.