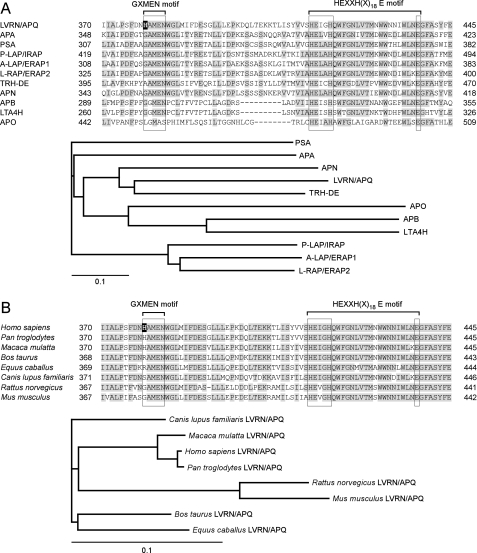
FIGURE 1.
Molecular evolution of LVRN/APQ. Alignments of the human LVRN/APQ amino acid sequence with the sequences of other human M1 aminopeptidases (A, upper) and its orthologues (B, upper) are shown. Amino acid sequence alignments around the GXMEN and HEXXH(X)18E motifs of M1 aminopeptidases are shown. Gaps are inserted into the sequence to obtain optimal alignments. Residues conserved among more than six enzymes are shaded. His379 residue of human LVRN/APQ is boxed in black. Evolutionary relationships of human M1 aminopeptidases (A, lower panel) and LVRN/APQ orthologues (B, lower panel) are shown. The bar shown below the phylogenetic tree represents the genetic distance. The sequence data used for analyses are as follows: A, LVRN/APQ (NM_173800) (18); APA (NM_001977) (46, 47); PSA, puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (NM_006310) (48); P-LAP/IRAP, placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase/insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (NM_005575) (3); A-LAP/ERAP1, adipocyte-derived leucine aminopeptidase/endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 (NM_001040458) (49); L-RAP/ERAP2, leukocyte-derived arginine aminopeptidase/endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-2 (NM_022350) (9); TRH-DE, thyrotropin-releasing hormone-degrading enzyme (NM_013381) (50); APN (NM_001150) (51); APB, aminopeptidase B (NM_020216) (52); LTA4H, leukotriene A4 hydrolase (NM_000895) (53); and APO, aminopeptidase O (NM_032823) (54). B, human (Homo sapiens, NM_173800), monkeys (Pan troglodytes, XM_001149318, and Macaca mulatta, XM_001086413), cattle (Bos taurus, XM_001788658), horse (Equus caballus, XM_001918093), dog (Canis lupus familiaris, XM_538554), rat (Rattus norvegicus, XM_577617), and mouse (Mus musculus, XM_911283).