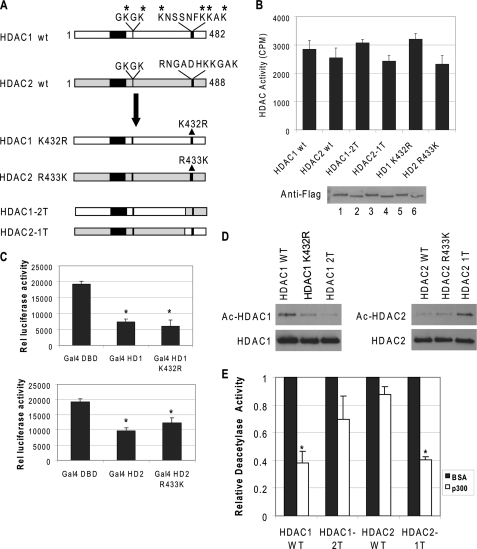
FIGURE 3.
C-terminal sequences of HDAC1 are important for acetylation. A, schematic representation of wild type (wt) and mutant HDAC1 and HDAC2 constructs. B, mutations on HDAC1 or HDAC2 do not affect deacetylase activity. Equal amounts of purified proteins were used to determine deacetylase activity and were analyzed by Western blot using FLAG antibody. The results are the average of three independent experiments ± S.D. Bottom panel, the level of recombinant proteins by Coomassie stain. Lane 1, wild type HDAC1; lane 2, wild type (wt) HDAC2; lane 3, HDAC1–2T; lane 4, HDAC2–1T; lane 5, HDAC1 K432R; and lane 6, HDAC2 R433K. C, mutations do not affect HDAC1 or HDAC2 function in vivo. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with a luciferase reporter driven by a minimal thymidine kinase promoter with four copies of the GAL4 DNA-binding sites. The fusions of the GAL4 DNA binding domain to HDAC1 (top panel), HDAC2 (bottom panel), or various mutants were cotransfected, and the effects on luciferase expression were determined. The results are the average of three independent experiments ± S.D. D, C-terminal sequences of HDAC1 are important for acetylation. FLAG-tagged HDAC1, HDAC2, or mutant proteins were incubated with purified p300 and acetyl-CoA. The products were then analyzed by Western blot with antibodies specific for acetyl-lysine and HDAC1 (left panel) or HDAC2 (right panel). E, acetylated HDAC2–1T lost deacetylase activity. The wild type and mutant proteins were acetylated with p300 or mock-acetylated with bovine serum albumin. The reaction products were then subjected to deacetylase assay. The relative deacetylase activity of HDACs treated with p300 was normalized with the deacetylase activity of the enzyme treated with bovine serum albumin. The results are the average of three independent experiments ± S.D. Asterisk indicates significant difference (Student's t test, p < 0.01).