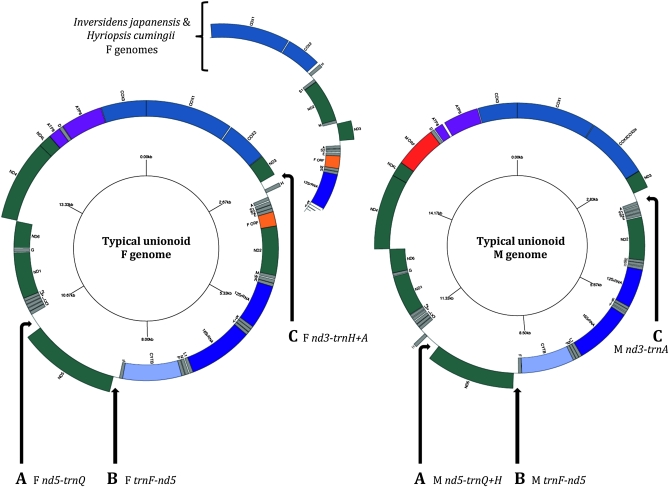
Figure 1.—
Gene maps of the gender-associated mitochondrial genomes of unionoid mussels. Gene identities: nd1–6 and nd4l, NADH dehydrogenase subunits 1–6 and 4L (complex I in green); cytb, cytochrome b (complex III in light blue); cox1-3, cytochrome c oxidase subunits I–III (complex IV in blue); atp6 and atp8, ATP synthase subunits 6 and 8 (complex V in light purple); 12SrRNA and 16SrRNA, small and large subunits of ribosomal RNA (in purple). Transfer RNA genes (in gray) are depicted by one-letter amino acid codes; L1, L2, S1, and S2 are differentiated by their anticodon sequences CUA, UAA, AGA and UCA, respectively. F ORF, F-specific open reading frame (orange); M ORF, M-specific open reading frame (red). Genes positioned inside the white circle are encoded on the light strand and genes outside the circle are encoded on the heavy strand. Arrows A, B, and C indicate shared unassigned regions >20 bp between F and M unionoid genomes [i.e., A, nd5–trnQ (this region contains trnH in M genomes); B, trnF–nd5; and C, between nd3–trnA (this region contains trnH in P. grandis, Q. quadrula, and V. ellipsiformis F genomes)].