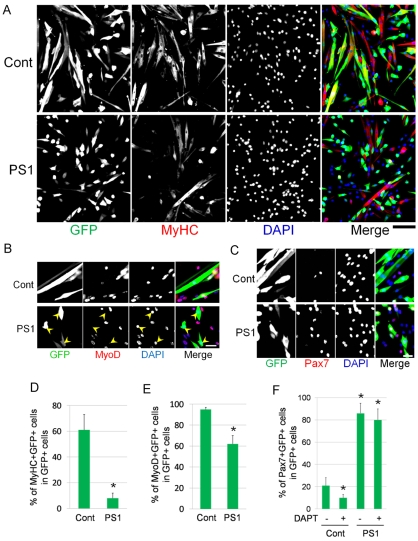
Fig. 3.
Constitutive PS1 expression leads to suppression of myogenic differentiation and augmentation of Pax7 expression. The effects of PS1 on satellite cell function were examined by constitutively expressing PS1 using expression vectors. (A,B) Primary satellite-cell-derived myoblasts were transfected with either control pMSCV-IRES-GFP (Cont) or pMSCV-PS1-IRES-GFP (PS1) vectors and, 48 hours later, immunostained for eGFP (to identify transfected cells) and either MyHC (A) or MyoD (B) (arrowheads indicate GFP+MyoD– cells in PS1-vector-transfected cells). (D,E) Constitutive PS1 expression significantly reduced the percentage of transfected cells that co-expressed either MyHC (D), or MyoD (E). (C,F) Constitutive PS1 expression also increased the percentage of satellite-cell-derived myoblasts expressing Pax7. (F) Although exposure of control pMSCV-IRES-GFP-transfected cells to 1 μM DAPT reduced the percentage of Pax7-expressing cells, DAPT inhibition of γ-secretase did not prevent the significant increase of Pax7 in transfected cells containing pMSCV-PS1-IRES-GFP vector. Data from at least three independent experiments is shown ± s.d. Asterisks in D-F indicate that data are significantly different from control values (P<0.05). Scale bars: 100 μm (A) and 30 μm (B,C).