Figure 2.
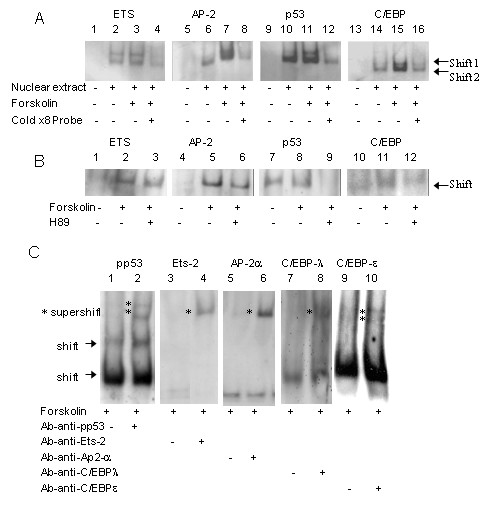
Effect of forskolin on JAR nuclear protein binding to oligonucleotides corresponding to MMP-2 promoter binding sites. A, binding of nuclear proteins, extracted from JAR cells cultured with or without Forskolin (10 μM), to dig-labeled oligonucleotides corresponding to consensus binding sites in the MMP-2 promoter was assessed with EMSA. The specificity of the DNA-protein complexes was tested by competing with a 8-fold excess unlabeled probe (lane 4, 8, 12, 16) The pictures are representative results of twelve different experiments. B, binding of nuclear proteins extracted from JAR cells treated with or without Forskolin (10 μM) and in the presence or absence of PKA inhibitor H89 to dig-labeled oligonucleotides was assessed with EMSA. The pictures are representative results of five different experiments. C, Specific antibodies against relevant transcription factors were added to the reaction mixture and EMSA supershift assay performed to detect transcription factors binding to the complex of dig-labeled oligonucleotides and nuclear proteins from JAR cells cultured with 10 μM Forskolin. Lane 1-2, addition of phosho-p53 (pp53) antibody to cell extract. Lane 3-4, Addition of Ets-2 antibody. Lane 5-6, Addition of Ap-2α antibody. Lane 7-8, Addition of C/EBPλ antibody and lane 9-10, addition of C/EBPε antibody to cells treated with Forskolin. Supershifted bands are designated with an asterisk (*). This result is representative of seven different experiments.
