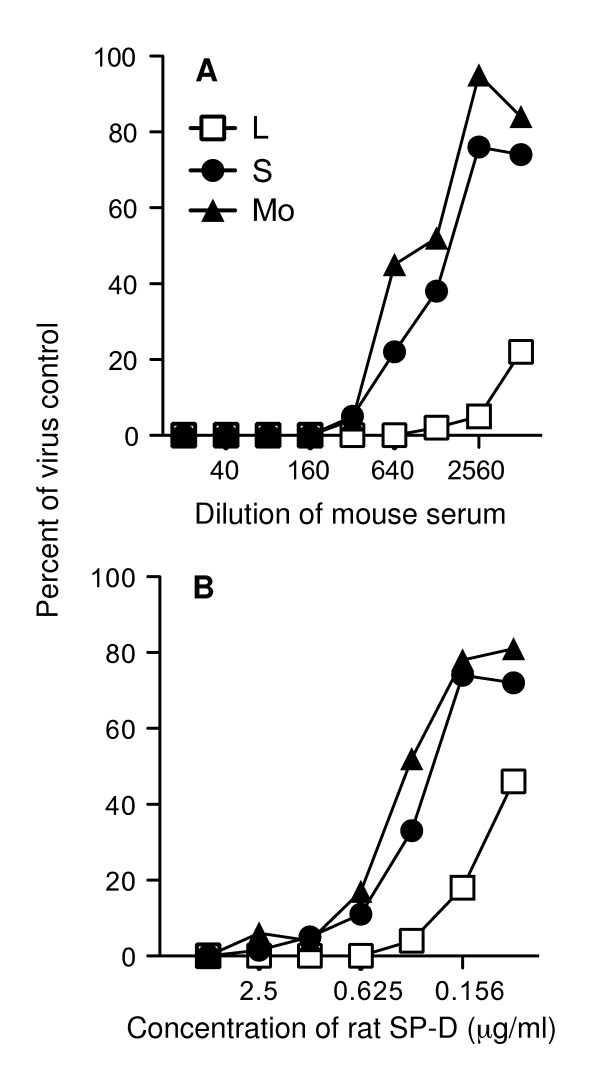
Figure 3.
Neutralization of plaque purified L, S and Mo clones of Beij/89 by the mannose-binding lectin in normal mouse serum and recombinant rat SP-D. L, S and Mo viruses were incubated with dilutions of (A) mouse serum or (B) rat SP-D for 30 mins at 37°C, and the amount of infectious virus remaining was determined by fluorescent focus assay. The total number of fluorescent foci in four representative fields were counted and expressed as a percentage of the number of foci in the corresponding area of duplicate control wells infected with virus alone ('Percent of virus control'). The neutralizing activity of 1/100 dilution of mouse serum or 1 μg/ml rat SP-D was inhibited by addition of 100 mM mannose to serum or SP-D prior to addition of virus (data not shown) demonstrating that the major neutralizing activity in each sample was a mannose-specific lectin.