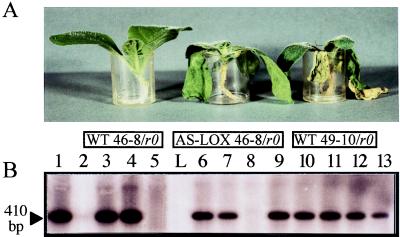
Figure 4.
Comparison of the phenotypes of WT and transgenic plants upon inoculation with Ppn race 0 (A). The transgenic IPM120-4 tobacco line was retained as an example. Plants were treated with nutrient solution (controls) or inoculated with a zoospore suspension (2 ml at 106 zoospores/ml) and were photographed 5 days postinoculation in the plastic beaker in which they were watered. From left to right: WT 46-8/r0, inoculated WT plant resistant to race 0; AS-LOX 46-8/r0, inoculated transgenic 120-4 plant; WT 49-10/r0, inoculated WT plant susceptible to race 0. (B) Detection of Ppn in the roots of inoculated plants by PCR amplification of the elicitin gene of the fungus. Three days postinoculation, total DNA was extracted from the upper part of the roots and subjected to PCR amplification. Ten microliters of the amplification products was separated on a 1.8% agarose gel and hybridized with 200 ng of the radiolabeled 410-bp elicitin product as a probe. Control experiments were performed on the following templates: lane 1, race 0 DNA (250 pg); lane 2, 46-8 WT plant DNA (500 ng); lane 3, 46-8 WT plant DNA (500 ng) plus race 0 DNA (250 pg). PCR assays on inoculated material were performed on DNA (500 ng) extracted from plant lines 49-10 WT (lane 4), 46-8 WT (lane 5), 120-1 to -4 (lanes 6–9), and 125-1 to -4 (lanes 10–13). L, molecular weight marker.