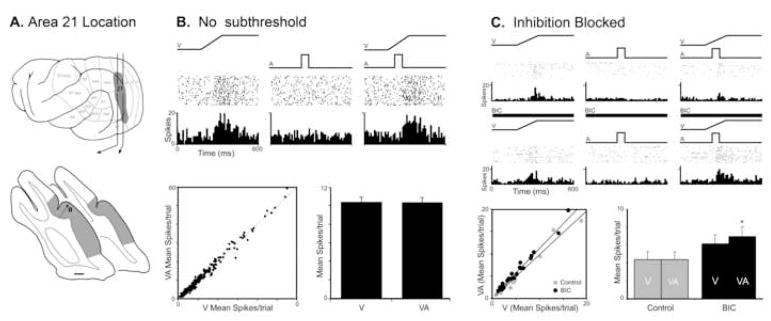
Figure 4. Auditory influences on visual activity in ferret visual Area 21.
Part ‘A’ illustrates, on the lateral view of the ferret cerebral cortex, the location of the visual fields including Area 21, as well as the position of Area 21 (shaded gray on coronal sections) surrounding the posterior aspects of the lateral sulcus. The line/black dot represent the recording penetration and site (respectively) of neurons whose activity is depicted in subsequent parts. Part ‘B’ shows the activity (raster 1 dot=1 spike; histogram=10ms time bins) of an Area 21 neuron in response to a visual (ramp labeled ‘V’), but not to an auditory (square wave labeled ‘A’) stimulus; combined visual-auditory stimulation did not elicit a significant response change. The scatter plot in ‘B’ for the population of Area 21 neurons shows the relationship of activity elicited by visual stimulation alone (x-axis) versus that evoked by the combined visual-auditory stimuli (y-axis). Nearly all neurons had responses that plotted close to the line of unity (48% above, 52% below), and the average response of the population was unchanged between the visual only and the visual-auditory stimulus conditions. Part ‘C’ shows an Area 21 neuron that was responsive to visual stimulation, but not auditory and, when the stimuli were combined, there was a modest reduction in response. However, when the same neuron was tested in the presence of the inhibitory transmitter antagonist Bicuculline methiodide (thick black bar), the response to the combined visual-auditory stimulus was significantly greater than that elicited by the visual stimulus alone The blockade of inhibition had a similar effect on the population of Area 21 neurons, where the responses of most neurons now plotted above the line of unity (C: scatter plot) and the average spikes per trial significantly (C: bar graph; *= p<005) increased in the combined versus visual-only condition.