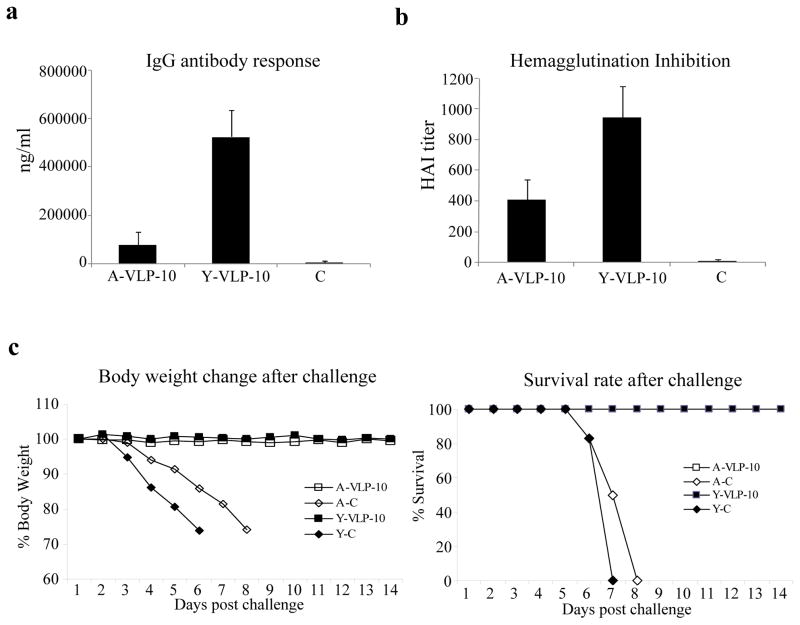
Figure 3. Immunization with influenza VLPs induced strong antibody responses and conferred effective protection against lethal influenza virus challenge in both young and aged mice.
Groups of young and aged mice (6 per group, 8-weeks old and 18-months old respectively) were immunized twice at 4-week intervals by IM injection of 10 μg influenza VLPs. The control groups received PBS only. Blood samples were collected at 2 weeks after the second immunization and analyzed for antibody responses against influenza virus. (a). IgG antibody responses against the influenza virus HA. The levels of antibody responses against HA were determined by ELISA using purified HA proteins as coating antigens, and expressed as the amount of HA-specific antibodies in 1 ml of serum samples (ng/ml). Error bars indicate standard deviations for each group. A-VLP-10, aged mice immunized with 10 μg VLPs; Y-VLP-10, young mice immunized with 10 μg VLPs; control, sera from young and aged control group mice. (b). Inhibition of hemagglutination by sera from immunized mice. The ability of sera to inhibit hemagglutination by influenza virus A/PR/8/34 were determined and expressed as the highest dilution that resulted in complete inhibition of hemagglutination (HAI titer). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. (c). Mouse survival rate and body weight change after lethal influenza virus challenge. At 4 weeks after the second immunization, mice were challenged by intranasal instillation of 10x LD50 of mouse-adapted influenza virus A/PR/8/34. Mice were monitored and weighed daily after challenge, and were sacrificed when found to display severe signs of illness or loss more than 25% body weight in accordance with IACUC guidelines. A-VLP-10, aged mice immunized with 10 μg VLPs; Y-VLP-10, young mice immunized with 10 μg VLPs; Y-C, control group of young mice; A-C, control group of aged mice.