Figure 1.
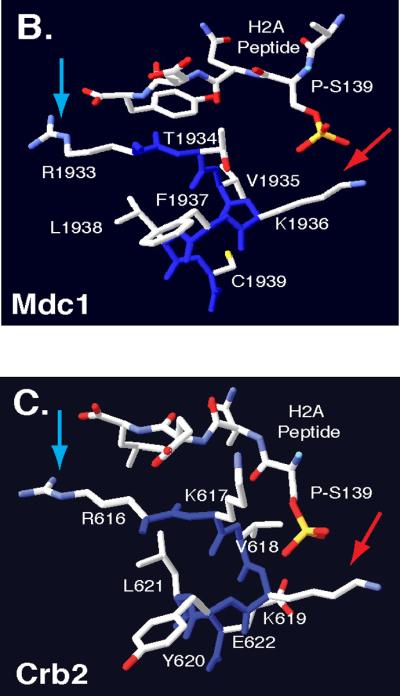
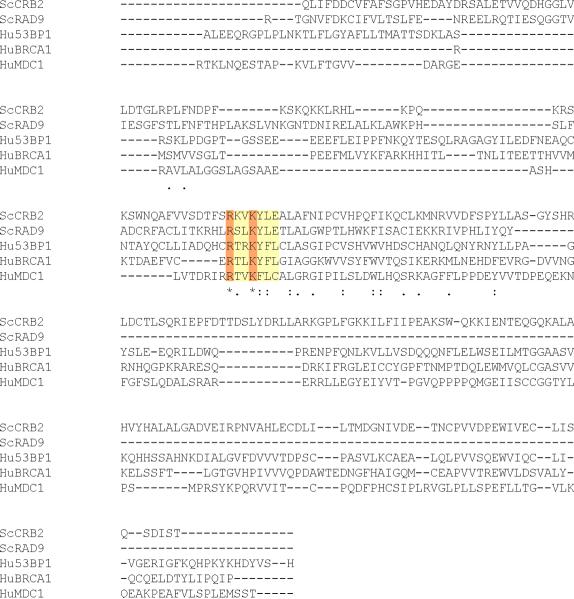
Comparative Protein Modeling for the Rad9 BRCT domain. (A)T-Coffee alignment of BRCT sequences from multiple checkpoint adaptor proteins identified a functionally conserved region, highlighted by a yellow box. Adaptor protein BRCT sequences include: S. pombe Crb2 (537–778), S. cerevisiae Rad9 (994–1122), Homo sapiens 53BP1 (1719–1977), H. sapiens BRCA1 (1649–1859) and H. sapiens MDC1 (1719–1977). Conserved arginine and lysine residues are highlighted in red. Crystal structures of MDC1 (B) and Crb2 (C) BRCT domains, in complex with a phospho-H2A peptide [66, 71]. Blue arrows denote conserved arginine residues that may contact the H2A carboxyl-terminal tail. Red arrows denote conserved lysine residues that may contact phosphoserine residues within the H2A tail. Backbone molecules are highlighted in dark blue, Nitrogen molecules are featured in light blue, oxygen molecules are featured in red and sulfur molecules are featured in yellow.