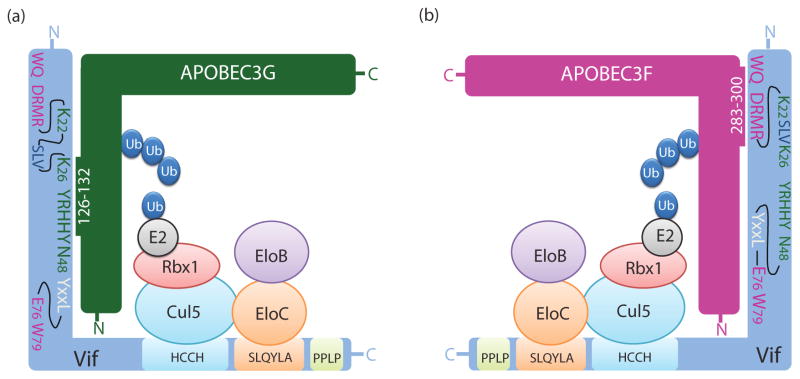
Figure 3.
Vif interactions with A3G, A3F, and the E2 ubiquitin ligase complex. (a and b) Amino acids in Vif that are involved in interaction with A3G but do not influence interaction with A3F are shown in dark green. Amino acids in Vif that are involved in interaction with A3F but do not influence interaction with A3G are shown in fuchsia. Only amino acids that reduced activity to <50% against A3G/A3F, but retained >80% activity against the other APOBEC3 protein are shown. The 69YXXL72 motif (white) interacts with both A3G and A3F and is shown in white. The 23SLV25 motif (dark blue) does not affect binding to A3G or A3F but is involved in A3G/A3F degradation. The E3 ubiquitin ligase complex consists of Cullin 5 (Cul5), Elongin B (EloB), Elongin C (EloC), RING finger protein 1 (Rbx1), and an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2). The HCCH motif in Vif (108Hx5Cx17–18Cx3–5H139) binds to Cul5 and the 144SLQYLA149 motif binds to EloC and EloB. Ubiquitin (Ub) is ligated to A3G and A3F by the E3 ubiquitin ligase. The 161PPLP164 motif is involved in Vif oligomerization. A3G amino acids 126–132 are involved in interaction with Vif (a) whereas A3F determinants that interact with Vif are located to amino acids 283–300 (b).