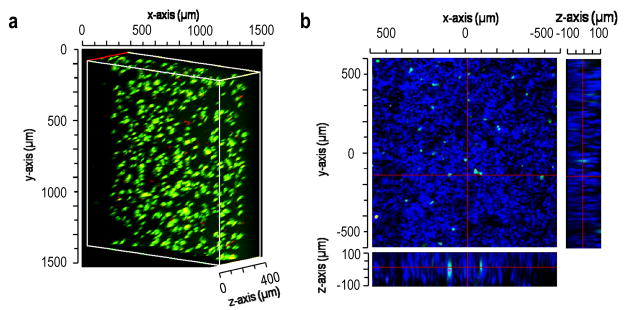
Figure 5.
Scaffolds could be formed in the presence of cells. (a) HepG2 cell viability in a scaffold composed of PEG8-VS/PEG8-amine microspheres, PEG8-acrylate/PEG8-amine microspheres (blue) and PEG8-VS/BSA microspheres. The PEG8-acrylate/PEG8-amine microspheres were no longer detectable, demonstrating complete hydrolysis of porogenic microspheres. HepG2 cells were stained with fluorescein diacetate (green; live) and ethidium bromide (red; dead). (b) HepG2 cell viability in a scaffold similar to (a) but composed of PEG8-VS/PEG8-amine microspheres, PEG8-VS/BSA microspheres (blue) and PEG8-acrylate/PEG8-amine microspheres. HepG2 cells were evenly dispersed throughout the macroporous scaffold and were surrounded by microspheres but not encapsulated in them. Live/dead assays were performed 48 h after scaffold formation to allow porogen dissolution, revealing cell viability of 91.9 ± 1.87% (n=3). Cells were imaged by confocal microscopy with a 10X objective.