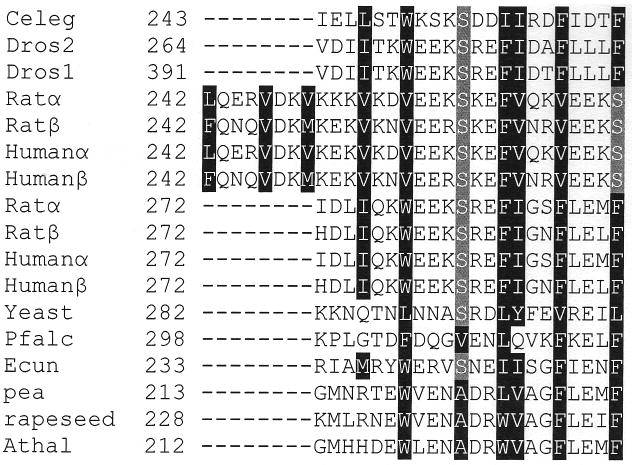
Fig. 6.
Putative amphipathic alpha helices of various CCT isoforms. Hydrophobic amino acids that plot on the hydrophobic face of the putative amphipathic alpha helix are boxed in black. The serine residues boxed in grey also plot on the hydrophobic face of the alpha helix. Rat and human CCTs contain an extended putative alpha helix with sequence repeats that is depicted in two halves. Celeg is C. elegans CCT (accession NP_001033540), Dros2 is D. melanogaster CCT2 (accession NP_647622), Dros1 is D. melanogaster CCT1 (accession NP_728628), Ratα is rat CCTα (accession NP_511177), Ratβ is rat CCTβ (accession NP_775174), Humanα is human CCTα (accession NP_005008), Humanβ is human CCTβ (accession NP_004836), Yeast is S. cerevisiae CCT (accession NP_011718), Pfalc is P. falciparum CCT (accession P49587), Ecun is E. cuniculi CCT (accession NP_586276), pea is P. sativum CCT (accession CAA70317), rapeseed is B. napus CCT (accession BAA09642), and Athal is A. thaliana CCT (accession NP_193249).