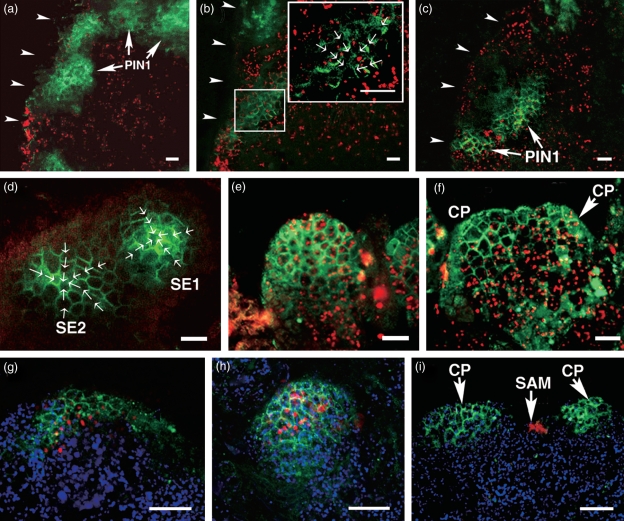
Figure 7.
Polar auxin transport indicated by a pPIN1::PIN1-GFP reporter. (a) PIN1 polarization does not occur in embryonic calli (EC) cultured in ECIM for 14 days. (b) After 16 h in SEIM, PIN1 localization is polarized to the edge region of embryonic callus. The inset is an enlargement of the box. The arrows show the direction of PIN1 polarization within cells. (c) Increased PIN1 polarization in embryonic callus in SEIM at 24 h. (d, e) Polar localization of PIN1 (green) in early and late globular somatic pro-embryos. The arrows show the direction of PIN1 polarization. (f) Signals in regional cells that will produce cotyledon primordia. (g) At 36 h in SEIM, the signals for WUS transcripts and PIN1 are co-localized in the same domain within the callus. (h) Co-localization of WUS transcripts and PIN1 in the somatic pro-embryo. (i) WUS transcripts are localized in the SAM, whereas PIN1 signals are localized in the cotyledon primordia. SE1 and SE2, regions that will produce somatic embryos; Co, cotyledon; CP, cotyledon primordia; SAM, shoot apical meristem. Arrowheads in (a)–(c) indicate the edge of calli. Green signals are PIN1. Red signals in (a)–(f) and blue signals in (g)–(i) are chlorophyll autofluorescence. The red color in (g)–(i) indicates WUS signals. In Scale bars = 50 μm (a–f) and 60 μm (g–i).