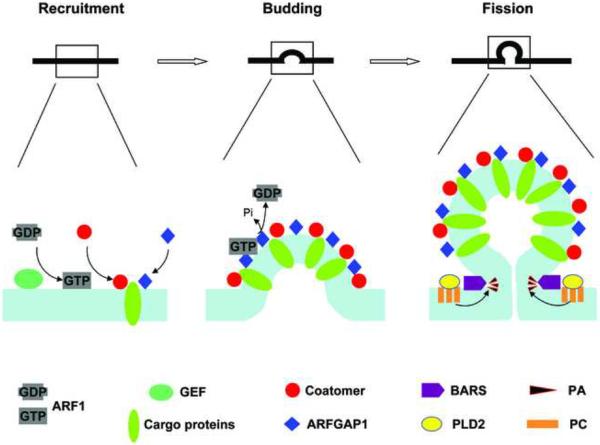
Figure 1.
Key components acting in COPI vesicle formation. For the initial step that involves the recruitment of key factors, GBF1 activates ARF1 and this process is likely to be facilitated by additional interactions with coatomer and cargo proteins. Subsequently, coatomer and ARFGAP1 act as coat components to drive both the early (budding) and late (fission) stage of vesicle formation. Their roles involve interaction with cargo proteins, which also achieves cargo sorting and thereby coupling vesicle formation with cargo sorting. For the fission stage, BARS in cooperation with PA are needed additionally. Not shown is the role of DAG, because its precise function in COPI vesicle formation remains to be resolved.