Figure 3. Palmitoylation sites of NR2A and NR2B.
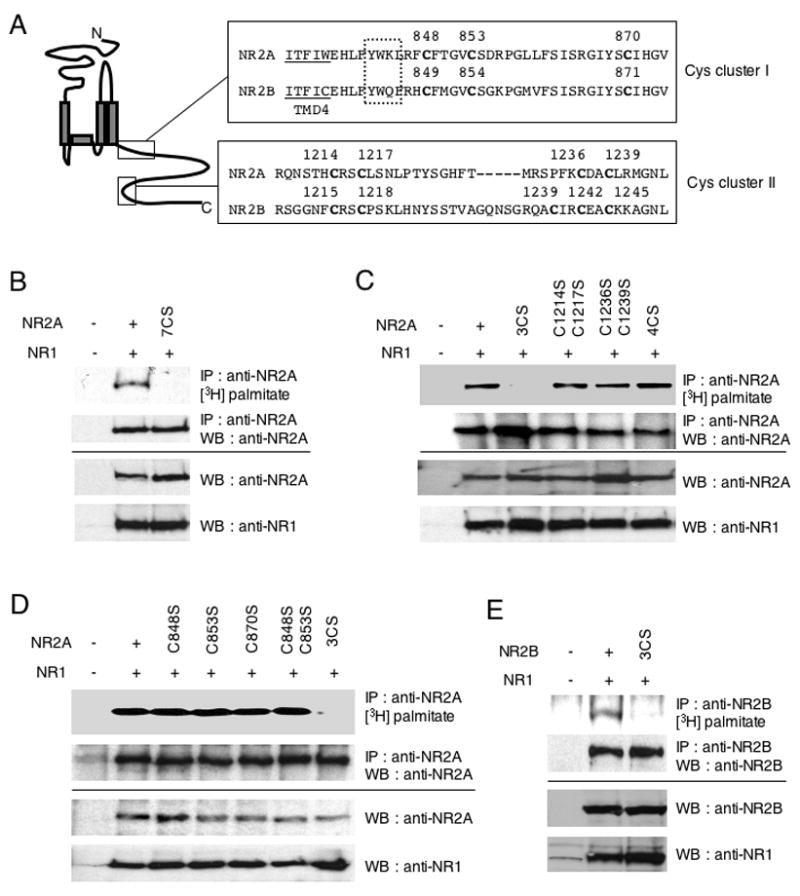
(A) C-terminal amino acid sequences of NMDA receptor subunits NR2A and NR2B, containing consensus cysteine clusters. Boxes indicate conserved cysteine residues (Cys cluster I and II). Transmembrane domain (TMD) 4 is underlined. Dotted box indicates AP-2 binding motif (YXXΦ). (B–E) Identification of NR2A and NR2B palmitoylation sites using a series of CS mutants. NR1/NR2A wild type and NR1/NR2A 7CS (B), or NR1/NR2A 3CS, NR1/NR2A C1214SC1217S, NR1/NR2A C1236SC1239S, NR1/NR2A 4CS (C), or NR1/NR2A C848S, NR1/NR2A C853S, NR1/NR2A C870S, NR1/NR2A C848SC853S, NR1/NR2A 3CS (D) and NR1/NR2B wild type and NR1/NR2B 3CS (E) were cotransfected into HEK 293T cells. Transfected cells were metabolically labeled with [3H]-palmitate and then solubilized and lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-NR2A or anti-NR2B antibodies. The incorporated [3H]-palmitate signals were shown (upper top). Immunoprecipitation (IP, second panels) and total protein expression (cell lysate) of each protein (third and fourth panels) was confirmed by western blotting (WB).
