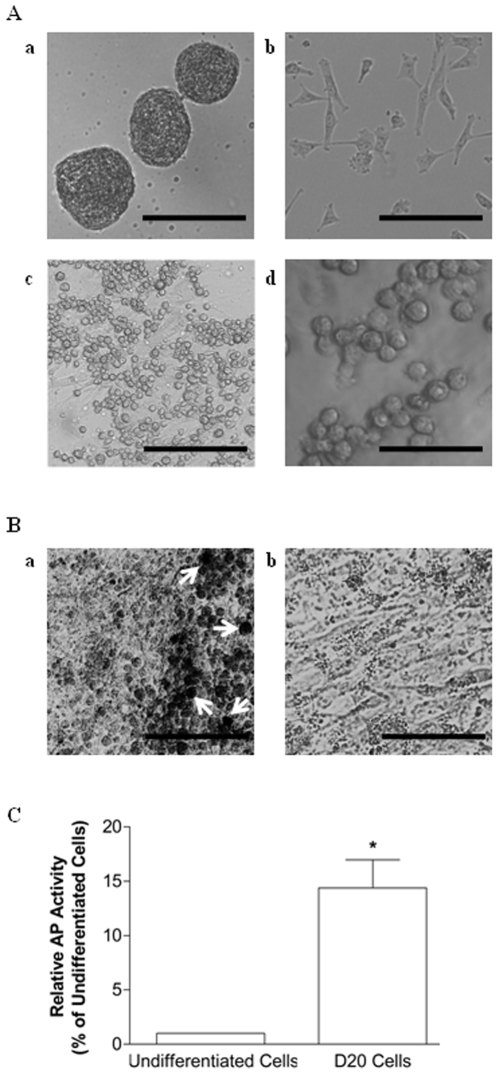
Figure 1. Morphology and AP activity of PGC-like cells differentiated from porcine skin-derived stem cells.
(A) Bright field images of (a) undifferentiated skin-derived stem cells maintained as spheres at passage 2 (100X) or (b) dissociated passage 2 skin stem cells after being plated in differentiation media for 24 hr in 60-mm dishes (100X). Loosely adherent or non-adherent putative PGCs at D20 of differentiation (c, d) could be distinguished from the somatic monolayer by their large size, round shape, and blebbing at (c) 100X and (d) 200X, respectively. (B) D20 differentiating cells, including a confluent monolayer with loosely adherent PGC-like cells, were fixed and stained for AP. Approximately 0.25% of the large, round PGC-like cells were AP-positive (a) compared to background levels associated with (b) the supporting somatic cell layer (100X). Size bar = 100 µm (Ad), 200 µm (Aa,b,c and B). (C) AP activity in undifferentiated skin-derived stem cells compared to D20 differentiating cells. A * denotes a statistical difference between the two groups (P<0.05). Absorbance values were normalized against total protein (mg/ml) and expressed as a percent relative to undifferentiated cells.