Figure 6.
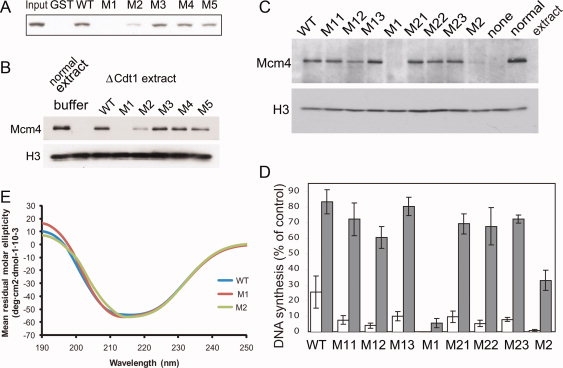
Interaction between mCdt1 and the MCM complex. (A) The association between mCdt1 and MCM complex. Purified MCM2,4,6,7 complex was incubated with various GST-mCdt1 mutant proteins (residues 177–557), and detected by Western blot using anti-MCM6. In M1 and M2 mutants, clusters of three residues (Arg481, Lys482, Thr486) and (Ser523, His525, Arg528) were simultaneously mutated, respectively. For M3, M4, and M5, the mutatons are V512A, L513A, and E516S, respectively. (B) The MCM loading activities of mCdt1 mutant proteins (M1 to M5: see text) onto chromatin were measured at 23°C, and compared to that of wild-type mCdt1. Normal extracts were used instead of Cdt1-depleted extracts for a sample applied on the lane “normal extract.” The data includes results of three independent experiments. Histone H3 was used for a loading control to show that equal amounts of chromatin were recovered in all lanes. (C) The MCM loading activities of Xenopus Cdt1 mutant proteins. The protocols are basically same as those in (B). M11, Lys543Ser; M12, Lys544Ser; M13, Thr548Ala; M1, Lys543Ser-Lys544Ser-Thr548Ala; M21, Ser585Ala; M22, His587Ser; M23, Arg590Ser; M2, Ser585Ala-His587Ser-Arg590Ser. (D) DNA synthesis activities of various Cdt1 mutant proteins. Values are indicated as percentages compared to that using buffer and normal extracts instead of Cdt1-mutant fractions and geminin extracts, respectively, after every values are subtracted by background value when buffer was used for Cdt1-fraction. Error bars indicated standard error of three independent experiments. (E) Analysis of conformational differences between the WT and mutant mCdt1CL proteins by circular dichroism. The spectra for mutant proteins, M1, and M2, are compared with that of a WT Cdt1CL protein. Because of the difficulties of obtaining mutant proteins with high purity (over 95%), we used Cdt1CL M1 and M2 (residues 420–557) mutant proteins to compare the conformational difference with the wild-type Cdt1CL.
