Figure 2.
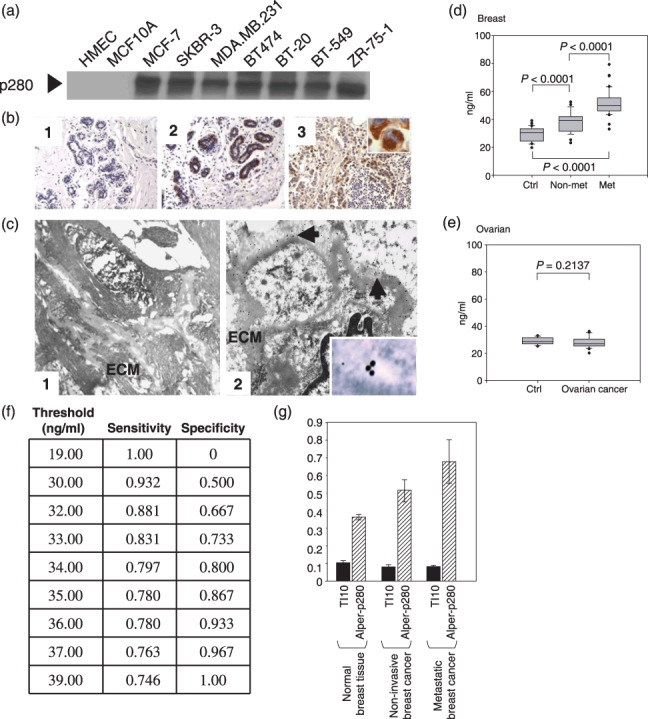
Filamin‐A protein levels are elevated in breast cancer cell lines, breast carcinoma tumor tissues, and in plasma collected from breast cancer patients. Alper‐p280 was used to western blot conditioned culture media of the indicated cell lines (a). Filamin‐A immunohistochemistry was done as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’. Two examples of Alper‐p280 staining in normal breast, one negative (panel 1) and one positive (panel 2), are shown. Alper‐p280 detected filamin‐A in invasive breast carcinoma (panel 3). The immunohistochemical staining for filamin‐A is granular and cytoplasmic (subcellular) (inset). Magnification, ×20 (b). Alper‐p280 was used to localize filamin‐A in ultra‐thin sections of normal breast tissue (panel 1) and non‐metastatic breast cancer (panel 2) using the immunogold labeling technique as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ followed by electron microscopy. Filamin‐A was below the level of detection in normal breast tissue. In non‐metastatic breast carcinoma, filamin‐A was present in the extracellular matrix (arrows), and within the vacuolar space (inset). (c). Box plot analysis representing levels of the 280‐kDa form of filamin‐A in plasma detected by the Alper‐p280 antibody and measured by ELISA in plasma. Soluble filamin‐A levels were determined by ELISA in plasma samples from females without breast cancer (Ctrl), non‐metastatic breast cancer (non‐met), and metastatic breast cancer (met). Soluble filamin‐A plasma concentrations were determined by generating a standard curve using normal human plasma spiked with known amounts of recombinant human filamin‐A. P‐values were determined by comparison with controls by anova. Data are representative of four independent experiments performed in triplicate. All analyses were done under blinded conditions (d). ELISA analyses of soluble filamin‐A levels in plasma from patients with ovarian serous cancer (stage II–IV, n = 20) were conducted as described in panel D (e). Threshold chart is described in the text (f). An ELISA assay was used to compare the reactivity of TI10 and Alper‐p280 against plasma samples isolated from normal controls, patients with non‐metastatic breast carcinoma, and patients with metastatic breast carcinoma. Five samples from each group were analyzed in duplicate. Data are mean ± SD.
